Back
Physics
Summer scholar reels in ‘STRIPED FISH’ for NIF
In high school, Liz Grace thought physics was boring and instead considered studying psychology or music. But then a college professor inspired Grace to see the wonders of physics. Today, as a National Ignition Facility (NIF) & Photon Science Summer Scholar, she’s helping to design and build a diagnostic instrument that could become a revolutionary measurement tool for…
PLS wraps up summer student programs
Approximately 1000 students came to the Laboratory this summer to engage in work-study employment in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, and administrative fields. PLS hosted a number of these students through its summer student programs (described below). Nuclear science and security The Glenn T. Seaborg Institute hosted 12 students this summer, including 8…
Improving the coherence of superconducting circuits
In an ideal superconducting quantum computer, the underlying quantum bits (qubits) are isolated from the noisy environment with no energy loss to mechanical or vibrational modes. However, in the real world, amorphous materials and material interfaces have defect states that cause qubits to lose their energy through vibrations and interactions with the surrounding…
Big Data Illuminates the Physical Sciences
Astrophysics is a growth area in the Laboratory’s advancement of basic science for national and global security needs. In this field, data science helps researchers catalog and interpret objects orbiting Earth and process huge volumes of data captured by ground- and space-based telescopes.
Shedding light on electron–laser interactions
When an electron encounters a laser pulse, it “wiggles” and radiates electromagnetic waves. As simple as this may sound, scientists have long struggled with an unresolved question: is the radiation energy provided by the laser or the electron? At low laser intensity, it has been experimentally confirmed that the radiation energy is entirely provided by the laser, while at…
Multilayer coatings for hard x rays
Multilayer interference mirrors are enabling components in x-ray optical systems. These mirrors consist of periodic or non-periodic structures of alternating thin film layers of two or more materials deposited on an optical substrate. Today’s applications and experimental facilities (including the National Ignition Facility) require novel, multilayer-based hard x-ray…
Sustained nuclear fusion in the Z pinch concept
Controlling nuclear fusion for power production is expected to require large and expensive magnetic coils or laser systems to create, heat, confine, and control the hot plasma needed to sustain fusion reactions. The idea of directly driving a column of plasma with an electrical discharge, known as Z pinch, was a simple and early method envisioned as a possible path to…
Livermore Leaps into Quantum Computing
As high-performance computing (HPC) systems evolve, the rate of progress is slowed by the physical limitations and power demands of conventional microchips. To overcome these obstacles, HPC experts currently pursue advances in parallel processing to increase overall performance and reduce energy consumption.
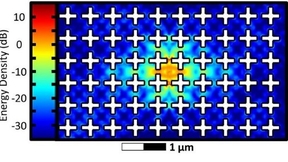
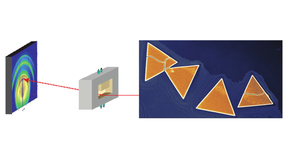
Probing silver nanocrystal superlattices
Typically, superlattices—faceted crystals composed of nanocrystal building blocks—have been made using slow evaporative techniques that often take days to weeks to form highly crystalline solids. This process is difficult to control, which has made it hard to systematically tune film properties and has hindered quantitative study of the assembly process. To overcome these…
Five researchers named to '40 Under 40' list
Five Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers join an eclectic group of entrepreneurs, writers, executives, philanthropists and more on Diablo Magazine’s annual "40 Under 40" list, which recognizes young professionals in the East Bay who are leading the charge in their fields. Louisa Pickworth, an experimental physicist and group leader in the Physics…
Learning to love science from gazing at planets
The moment Louisa Pickworth saw the rings of Saturn through her father’s backyard telescope, she knew she wanted to become a scientist to learn "more and more and more." Today, Pickworth, 32, is one of LLNL’s heralded young physicists for her work developing cutting-edge X-ray diagnostics to help scientists learn more about ultrahigh energy physics and inertial confinement…
Summer scholars learn value of team science
A group of NIF & Photon Science summer scholars and visiting graduate students are experiencing the value of teamwork as they conduct experiments at LLNL’s Jupiter Laser Facility (JLF). Jesus Hinojosa, 26, a University of Michigan graduate student, and Matthew Thibodeau, 21, a Rice University undergraduate, joined a team of veteran scientists and researchers to explore…
National Ignition Facility reveals how hydrogen becomes metallic inside gas giant planets
Swirling dense metallic hydrogen dominates the interiors of Jupiter, Saturn and many extra-solar planets. Building precise models of these giant planets requires an accurate description of the transition of pressurized hydrogen into this metallic substance — a long-standing scientific challenge. In a paper published today by Science, a research team led by scientists at…
Quest for source of black hole dark matter
Like a game of "hide and seek," Lawrence Livermore astrophysicists know that there are black holes hiding in the Milky Way, just not where. If they find them toward the galactic bulge (a tightly packed group of stars) and the Magellanic Clouds, then black holes as massive as 10,000 times the mass of the sun might make up dark matter. If they are only toward the galactic…
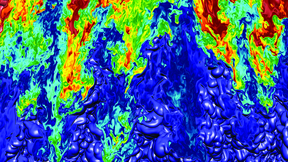
Researchers work to advance understanding of hydrodynamic instabilities in NIF, astrophysics
In a Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) "Special Feature" paper published online June 26, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and University of Michigan researchers reported on recent experiments and techniques designed to improve understanding and control of hydrodynamic (fluid) instabilities in high energy density (HED) settings such as…
Warhead life extension passes key milestone
The program to extend the life of the W80 nuclear warhead recently achieved a significant milestone when the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) gave passing grades to the plans to refurbish certain components and the proposed approach to developing component cost estimates. Passing the milestone confirms that the life extension program (LEP), dubbed the W80-4…
Cohen honored with computational plasma physics award
Retiree Bruce Cohen (PHYS) has been selected as the recipient of the 2018 IEEE Nuclear and Plasma Sciences Society’s Charles K. Birdsall Award for “contributions to the numerical simulation of plasmas, particularly multiple time-scale methods, and to their application to diverse plasma physics problems, from laser–plasma interactions to tokamaks.” The Birdsall Award…
Pushing Boundaries in Plasma Physics: Michael Campanell Brings His Revolutionary Model to LLNL
When Michael Campanell was a graduate student at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, he noticed something unusual: the boundary physics simulation he was running wasn’t behaving the way it was supposed to. A century of plasma theory predicted one thing, but Campanell’s simulation was doing another. This was the impetus for his thesis, and a big challenge to the status…
Concussion study may 'change the game'
Researchers have identified evidence of early chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) brain pathology after head impact -- even in the absence of signs of concussion. Early indicators of CTE pathology not only persisted long after injury but also spread through the brain, providing the best evidence to date that head impact, not concussion, causes CTE. The findings,…
LLNL releases newly declassified test videos
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) released 62 newly declassified videos today of atmospheric nuclear tests films that have never before been seen by the public. The videos are the second batch of scientific test films to be published on the LLNL YouTube channel this year, and the team plans to publish the remaining videos of tests conducted by…