Back
ASC
Lawrence Livermore-led effort one of nine DOE-funded data reduction projects
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory-led effort in data compression was one of nine projects recently funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) for research aimed at shrinking the amount of data needed to advance scientific discovery. LLNL was among five DOE national laboratories to receive awards totaling $13.7 million for data reduction in scientific applications…
DOE-funded project to advance portability of heterogenous HPC applications
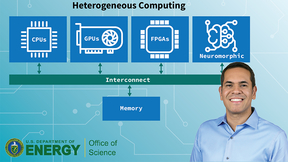
A project involving researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and national lab and academic collaborators has received U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) funding as part of an effort to adapt scientific software for next-generation high-performance computing (HPC) systems. The project, “ComPort: Rigorous Testing Methods to Safeguard Software Porting,” will…
Simulating nuclear cloud rise anywhere, anytime
For decades, understanding the behavior of a nuclear mushroom cloud was done with careful analysis of observations made during the testing era. Old photos, outdated film and incomplete weather data made precise calculations difficult. Now, with results published in Atmospheric Environment, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists are improving our…
LLNL/ATOM engagement with Purdue introduces students to drug design modeling
Through an engagement with Purdue University’s The Data Mine learning community, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Purdue are partnering to speed up drug design using computational tools under the Accelerating Therapeutic Opportunities in Medicine (ATOM) project. Over two recent semesters (fall 2020 and spring 2021), LLNL bioinformatics scientist and ATOM…
Video: Flux – enabling modern supercomputing workflows
This video describes Flux, an open-source software framework that manages and schedules computing workflows to maximize available resources to run applications faster and more efficiently.
ISC21 event calendar
Join LLNL at the virtual ISC High Performance Conference on June 24 through July 2 Lawrence Livermore will participate in the ISC High Performance Conference (ISC21) on June 24 through July 2. The online event brings together the HPC community—from research centers, commercial companies, academia, national laboratories, government agencies, exhibitors, and more—to share…
Secretary of Energy Jennifer M. Granholm virtually visits LLNL
U.S. Secretary of Energy Jennifer M. Granholm virtually visited Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) Friday, June 25, where she met with leading scientists and engineers, toured lab facilities and learned about key research efforts. Granholm, the nation’s 16th Secretary of Energy and only the second woman to lead the Department of Energy (DOE), is conducting…
DOE funds 13 new High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation projects
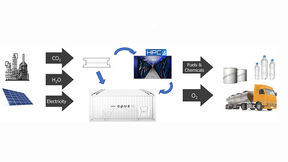
The Department of Energy (DOE) today announced awards of $3.7 million for 13 new High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) projects, including a collaboration involving Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) targeted at improving CO2 conversion. DOE’s Advanced Manufacturing Office (AMO) – an office within DOE’s Office of Energy Efficiency and…
Lawrence Livermore team looks at nuclear weapon effects for near-surface detonations
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has taken a closer look at how nuclear weapon blasts close to the Earth’s surface create complications in their effects and apparent yields. Attempts to correlate data from events with low heights of burst revealed a need to improve the theoretical treatment of strong blast waves rebounding from hard surfaces. This led…
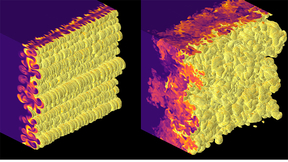
Scientists identify key trends in high-energy-density mixing layers
Imagine a bottle of salad dressing containing oil and vinegar. The oil has a lower density than vinegar, so it floats on the vinegar. The oil will not stay trapped under the vinegar if the bottle is flipped upside down. It will bubble up through the vinegar until a stable state is restored. This simple physical process is known as Rayleigh–Taylor instability, and it can be…
Advanced Data Analytics for Proliferation Detection shares technical advances during two-day meeting
The Advanced Data Analytics for Proliferation Detection (ADAPD) program held a two-day virtual technical exchange meeting recently. The goal of the meeting was to highlight the science-based and data-driven analysis work conducted by ADAPD to advance the state-of-the-art to accelerate artificial intelligence (AI) innovation and develop AI-enabled systems to enhance the…
LLNL, IBM and Red Hat joining forces to explore standardized HPC resource management interface
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), IBM and Red Hat are combining forces to develop best practices for interfacing high performance computing (HPC) schedulers and cloud orchestrators, an effort designed to prepare for emerging supercomputers that take advantage of cloud technologies. Under a recently signed memorandum of understanding (MOU), researchers aim to…
De Supinski named one of HPCwire’s 'People to Watch'
Bronis R. de Supinski, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) chief technology officer (CTO) for Livermore Computing (LC), is one of the top influencers in the high performance computing industry for 2021, according to HPCwire. On April 7, the publication honored de Supinski as one of its "People to Watch," a group of 14 “innovators and visionaries building and…
COVID-19 HPC Consortium reflects on past year
COVID-19 HPC Consortium scientists and stakeholders met virtually on March 23 to mark the consortium’s one-year anniversary, discussing the progress of research projects and the need to pursue a broader organization to mobilize supercomputing access for future crises. The White House announced the launch of the public-private consortium, which provides COVID-19 researchers…
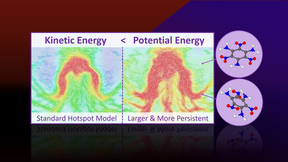
Research uncovers missing physics in explosive hotspots
Research conducted on Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) supercomputer Quartz highlights findings made by scientists that reveal a missing aspect of the physics of hotspots in TATB (1,3,5-trimamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene) and other explosives. Hotspots are localized regions of elevated temperature that form from shock-induced collapse of microstructural…
'Self-trained' deep learning to improve disease diagnosis
New work by computer scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and IBM Research on deep learning models to accurately diagnose diseases from X-ray images with less labeled data won the Best Paper award for Computer-Aided Diagnosis at the SPIE Medical Imaging Conference on Feb. 19. The technique, which includes novel regularization and “self-training”…
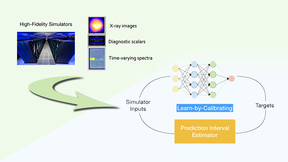
Lab researchers explore ‘learn-by-calibration’ approach to deep learning to accurately emulate scientific process
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) computer scientists have developed a new deep learning approach to designing emulators for scientific processes that is more accurate and efficient than existing methods. In a paper published by Nature Communications, an LLNL team describes a “Learn-by-Calibrating” (LbC) method for creating powerful scientific emulators that…
Lawrence Livermore computer scientist heads award-winning computer vision research
The 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV 2021) on Wednesday announced that a paper co-authored by a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) computer scientist received the conference’s Best Paper Honorable Mention award based on its potential impact to the field. The paper, titled "Generative Patch Priors for Practical Compressive…
LLNL’s de Supinski earns prestigious IEEE Fellowship
IEEE, the world's largest technical professional organization, announced it has elevated Bronis de Supinski to the rank of fellow, recognizing Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's (LLNL) Livermore Computing’s chief technology officer (CTO) for his leadership in the design and use of large-scale computing systems. The prestigious IEEE fellow distinction, which takes…
LLNL, IBM win SC20 ‘Test of Time’ for Blue Gene/L
A team of current and former Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and IBM scientists won the annual “Test of Time” award at the 2020 Supercomputing Conference on Nov. 19 for a paper outlining LLNL’s Blue Gene/L supercomputer. Published by the Supercomputing Conference in 2002, the paper was the first peer-reviewed overview article to disclose details of Blue Gene…