Back
HPC, Simulation, and Data Science
Registrations ongoing for virtual forum on industrial machine learning applications
Registration is open through July 29 for the first-ever Machine Learning for Industry Forum (ML4I), a three-day virtual event starting Aug. 10. The forum aims to foster and illustrate the adoption of machine learning methods for practical industrial outcomes, with a strong emphasis on manufacturing. Over the course of the event, attendees will engage in dialog about…
LLNL and collaborators improve electrochemical reactor performance through 3D printing
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and their collaborators are leveraging the power of 3D printing to improve the performance of electrochemical reactors used to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) to useful energy sources, chemicals and material feedstocks. Working under a cooperative research and development agreement (CRADA) with Stanford University and…
New research proves quantum computing errors correlated, ties them to cosmic rays
Research by a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) physicist and a host of collaborators is shedding new light on one of the major challenges to realizing the promise and potential of quantum computing — error correction. In a new paper published in Nature and co-authored by LLNL physicist Jonathan DuBois, scientists examined quantum computing stability,…
Virtual LLNL-UC Merced Data Science Challenge tackles asteroid detection though machine learning
Over three weeks, students from the University of California, Merced collaborated online with mentors at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) to tackle a real-world challenge problem: using machine learning to identify potentially hazardous asteroids that could pose an existential threat to humanity. The Data Science Challenge was the third such annual event for…
Lawrence Livermore team looks at nuclear weapon effects for near-surface detonations
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has taken a closer look at how nuclear weapon blasts close to the Earth’s surface create complications in their effects and apparent yields. Attempts to correlate data from events with low heights of burst revealed a need to improve the theoretical treatment of strong blast waves rebounding from hard surfaces. This led…
Lawrence Livermore team looks at nuclear weapon effects for near-surface detonations
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has taken a closer look at how nuclear weapon blasts close to the Earth’s surface create complications in their effects and apparent yields. Attempts to correlate data from events with low heights of burst revealed a need to improve the theoretical treatment of strong blast waves rebounding from hard surfaces. This led…
Lab postdocs invited to prestigious Heidelberg Forum
Two Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) postdoctoral researchers are among a select group of 200 scientists invited to attend the 8thHeidelberg Laureate Forum, an international conference that connects young researchers with laureates of the major prizes in mathematics and computer science. For a week in September, LLNL computational engineering postdocs Ruben…
Conference papers highlight importance of data security to machine learning
The 2021 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, the premier conference of its kind, will feature two papers co-authored by a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researcher targeted at improving the understanding of robust machine learning models. Both papers include contributions from LLNL computer scientist Bhavya Kailkhura and examine the…
Students build knowledge of machinist trade during Lab's first-ever virtual Manufacturing Workshop
The COVID-19 pandemic didn’t prevent local high school students from learning what it’s like to be one of the more than 150 machinists who work at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) during the Materials Engineering Division’s (MED) Manufacturing Workshop, held April 20-22. Students attended the three-day workshop virtually after their school days ended, where…
Advanced Data Analytics for Proliferation Detection shares technical advances during two-day meeting
The Advanced Data Analytics for Proliferation Detection (ADAPD) program held a two-day virtual technical exchange meeting recently. The goal of the meeting was to highlight the science-based and data-driven analysis work conducted by ADAPD to advance the state-of-the-art to accelerate artificial intelligence (AI) innovation and develop AI-enabled systems to enhance the…
Lawrence Livermore takes part in international planetary defense conference
Ten scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) last week took part in the 7th IAA Planetary Defense Conference (PDC), hosted by the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs in cooperation with the European Space Agency. Megan Bruck Syal, who helped lead the Lab’s participation in the event and who also was a conference session chair, said this year…
HPC4Energy Innovation kicks off spring solicitation
The Department of Energy’s High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) Initiative is accepting industry proposals for projects leveraging the world-class supercomputing and expertise of DOE national laboratories to address key energy-related challenges in domestic manufacturing. The DOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy’s Advanced Manufacturing…
Krell Institute honors Hittinger with Corones Award
The Krell Institute, a nonprofit organization serving the scientific and educational communities, has awarded Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) computational scientist Jeff Hittinger with its 2021 James Corones Award in Leadership, Community Building and Communication. The award, named for the institute’s founder, recognizes mid-career scientists and engineers…
LLNL, IBM and Red Hat joining forces to explore standardized HPC resource management interface
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), IBM and Red Hat are combining forces to develop best practices for interfacing high performance computing (HPC) schedulers and cloud orchestrators, an effort designed to prepare for emerging supercomputers that take advantage of cloud technologies. Under a recently signed memorandum of understanding (MOU), researchers aim to…
Lab offers forum on machine learning for industry
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is looking for participants and attendees from industry, research institutions and academia for the first-ever Machine Learning for Industry Forum (ML4I), a three-day virtual event starting Aug. 10. Pre-registrations are open for the forum, which aims to foster and illustrate the adoption of machine learning methods for…
Bay Area labs to host business partnership event
Three-day virtual event will showcase how businesses can tap into national labs' resources Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Sandia National Laboratories, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, as part of the Bay Area Lab Innovation Networking Center (LINC), will showcase partnership mechanisms at a three-day event…
De Supinski named one of HPCwire’s 'People to Watch'
Bronis R. de Supinski, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) chief technology officer (CTO) for Livermore Computing (LC), is one of the top influencers in the high performance computing industry for 2021, according to HPCwire. On April 7, the publication honored de Supinski as one of its "People to Watch," a group of 14 “innovators and visionaries building and…
COVID-19 HPC Consortium reflects on past year
COVID-19 HPC Consortium scientists and stakeholders met virtually on March 23 to mark the consortium’s one-year anniversary, discussing the progress of research projects and the need to pursue a broader organization to mobilize supercomputing access for future crises. The White House announced the launch of the public-private consortium, which provides COVID-19 researchers…
Novel deep learning framework for symbolic regression
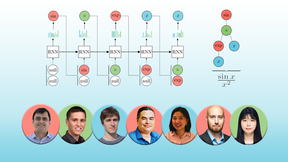
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) computer scientists have developed a new framework and an accompanying visualization tool that leverages deep reinforcement learning for symbolic regression problems, outperforming baseline methods on benchmark problems. The paper was recently accepted as an oral presentation at the International Conference on Learning…
Lab event encourages growth of women in data science
Coinciding with International Women’s Day on March 8, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s 4th Women in Data Science (WiDS) regional event brought women together to discuss successes, opportunities and challenges of being female in a mostly male field. The Lab’s first-ever virtual WiDS gathering attracted dozens of LLNL data scientists as well as some from outside the…