Back
Physical and Life Sciences
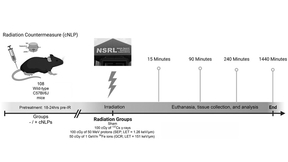
Developing radioprotection strategies for deep space exploration
During future missions beyond low Earth orbit (LEO), such as those planned to the moon, near-Earth asteroids, and Mars, astronauts will face poorly defined health risks as a result of exposure to the complex space ionizing radiation (IR) environment. In fact, the gastrointestinal (GI) system is documented to be highly radiosensitive with even relatively low dose IR…
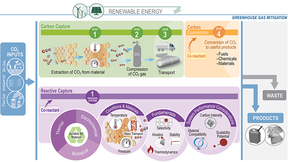
CO<sub>2</sub> capture and conversion perspectives for a cleaner future
To date, most CO2 capture and conversion processes have been developed in isolation, where the output of the capture process is purified, compressed CO2, which can be used as the feedstock for the CO2 conversion process. This is an energy intensive process and purified CO2 stream still needs to be delivered to the location where it will be converted to the desired product,…
Energy storage for the future
The need for efficient and sustainable energy storage systems is becoming increasingly crucial as the world transitions toward renewable energy sources. However, traditional energy storage systems have limitations, such as high costs, limited durability, and low efficiency. Therefore, new and innovative materials and technologies, such as aerogels (highly porous networks…
Defense Programs Awards of Excellence recognize innovation and achievements in 2021
In virtual ceremonies held May 4 and June 26, Marvin Adams, deputy administrator for Defense Programs at the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), honored individuals and teams at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and partner sites for their outstanding contributions to nuclear security. The Defense Programs Awards of Excellence recognition events…
New NIF experimental platform will probe warm dense matter
To learn about the properties of materials under changing temperatures and pressures, researchers typically combine laboratory experiments with theoretical models and computer simulations. It’s an iterative process: The models help in designing the experiments and interpreting the results, and the results “constrain,” or fine-tune, the models so they can effectively guide…
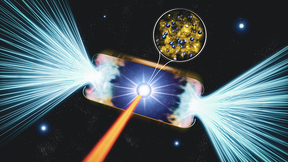
Sterile neutrino research ramps up
An international collaboration of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and other scientific institutions is ramping up its studies into “sterile neutrinos” to discover and better understand dark matter. Sterile neutrinos are theoretically predicted new particles that offer an intriguing possibility in the quest for understanding the dark matter in…
Advanced masking technology enables new applications for metasurface optics
Optics researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have refined their novel metasurface process to create taller features without increasing feature-to-feature spacing, an advance that unlocks exciting new design possibilities. “We have refined our process to create metasurfaces that allow for a wide optical bandwidth and a large span of incidence angles…
Human-caused climate change at the center of recent California wildfires
Summer wildfire seasons in California routinely break records. The average summer burn area in forests in northern and central portions of the state have increased fivefold between 1996 and 2021 compared to between 1971 and 1995. Although the drivers of increased temperature and dryness are known, the contribution of human-caused climate change to wildfire activity,…
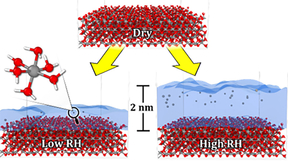
Research reveals how humidity affects atmospheric corrosion of aluminum metal
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) performed simulations using the Lab's supercomputer Ruby to uncover physical mechanisms that explain why humidity controls the rate of atmospheric corrosion of aluminum metal. Their research is featured in the ACS Journal of Applied Materials and Interfaces. Accurate predictions of aluminum component lifetimes…
Six Lab scientists partner with university researchers through WCI’s ACT Awards
Six scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory were recently granted awards through the Lab's 2022 Academic Collaboration Team (ACT) annual call for proposals. Now in their fourth year, ACT university collaboration awards were created to encourage and advance strategic partnerships among universities with a focus on the Lab’s and Weapons and Complex Integration’s…
Cover cropping can increase farming yields
Cropland management practices that restore soil organic carbon (SOC) are often looked at as climate solutions that also enhance yields. But how often these benefits align at the farm level — the scale of farmers’ decision-making — remains unclear. In a new study in Nature Sustainability, a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist and collaborators examined…
Three graduate students earn awards to work at Lawrence Livermore
Three graduate students have earned Department of Energy Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) Program awards to perform their doctoral dissertation research at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). They are three among the 87 graduate students representing 33 states for the SCGSR program’s 2022 Solicitation 2 cycle. Through world-class training and…
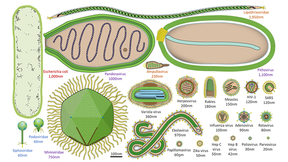
Researchers explore how viruses enhance our understanding of life in the universe
On Earth, viruses are abundant and an integral part of life. However, very little is known about them outside human health contexts, especially in areas related to space. Understanding the role viruses play on Earth and how they interact with their hosts in extreme environments can better inform human spaceflight missions (environmental control, life support systems, and…
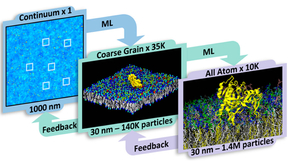
Next-generation simulation infrastructure bridges multiscale models
One of the fundamental challenges in computational modeling is to balance the trade-off between the length and time scales that need to be simulated and the corresponding computational costs. Relevant time scales are typically determined by a phenomena of interest, e.g., a protein’s activation or a chemical reaction, whereas length scales are usually chosen based on the…
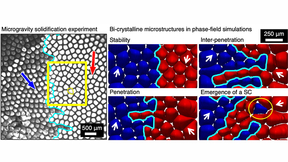
Microgravity experiments reveal metallurgical phenomena
In solidification processing, such as casting, welding, or additive manufacturing, cellular or dendritic patterns develop during the growth of a solid crystal from the liquid phase. In metallurgy, each similarly patterned region is referred to as a grain—which must be controlled during processing as grains affect structural performance. Additionally, the grain texture—the…
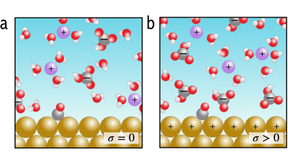
Microenvironment engineering for improved electrochemical reduction of CO<sub>2</sub>
Copper-based catalysts are highly active for electrochemical reduction of CO2 (CO2R) to several desirable hydrocarbon products, such as methane (CH4), formic acid (HCOOH), ethylene (C2H4), and ethanol (C2H5OH). CO2R is dually beneficial, as it allows for the conversion of excess atmospheric CO2 into useful chemicals. However, using copper-based catalysts for CO2R depends…
New report finds that carbon capture and storage in California can concurrently serve local communities, the environment and the economy
A new report co-authored by George Peridas of the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Benjamin Grove of the Clean Air Task Force examines the economic viability of carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects in California and finds that several classes of projects are viable today. These can help the state meet its climate goals and hold a sizable potential to…
Experiments shed light on pressure-driven ionization in giant planets and stars
Scientists have conducted laboratory experiments at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) that provide new insights on the complex process of pressure-driven ionization in giant planets and stars. Their research, published today in Nature, unveils the material properties and behavior of matter under extreme compression, offering important implications for…
Energy Inks wins regional FLC award
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)-developed technology known as Energy Inks has won a best in region award for the Far West region from the Federal Laboratory Consortium for Technology Transfer (FLC). This is the technology’s second award in the past nine months, as it received an R&D 100 award last September as one of the top 100 industrial inventions in…
Lab researchers assist for new Compact X-ray FEL
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and University of California, Davis researchers are assisting Arizona State University with a new laser facility that will use ultrafast pulsed X-ray beams to study biological processes, materials and other research at the atomic level. In March, the National Science Foundation announced that it was awarding $90.8 million to…