Back
Physical and Life Sciences
Cross-directorate team works to survey the Lab’s biodiversity
From the rolling hills of Tracy to the grassy plains of Livermore, LLNL’s lands are replete with biodiversity, and keeping track of the resident flora and fauna is no small feat. Acoustic monitoring was used to passively search for rare bat species. Wildlife biologists from ECORP Consulting are shown installing a Wildlife Acoustics SM4BAT-FS unit using the SMM-U2…
Water modified ancient asteroid
Samples from asteroid Ryugu returned by the Hayabusa2 mission contain evidence of extensive alteration by water and appear related to CI chondrites, which are believed to best represent the bulk of the solar system composition. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists in collaboration with an international team looked at the isotopic composition of oxygen,…
LLNL, University of California initiative fosters academic partnership
A new joint initiative between the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) Weapons and Complex Integration (WCI) Directorate and the University of California (UC) is aimed at developing next generation academic leadership with strong and enduring national laboratory connections. The LLNL Early Career UC Faculty Initiative is accepting proposals from untenured, tenure…
LLNL scientist named to Forbes ’30 under 30’ list
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory materials scientist Daniel Schwalbe-Koda has been named one of Forbes “30 under 30” for 2023 in the science category. Forbes features a list of 600 individuals under the age of 30 each year, who have impactful careers and/or accomplishments across a span of industries — healthcare, science, consumer technology, Hollywood, retail,…
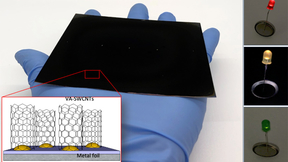
Charging up with carbon nanotubes
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have created vertically aligned single-walled carbon nanotubes on metal foils that could be a boon for energy storage and the electronics industry. Vertically aligned carbon nanotubes (VACNTs) have exceptional mechanical, electrical and transport properties in addition to an aligned architecture, which is key for…
Environmental DNA uncovers a 2-million-year-old ecosystem in Greenland
Around 2 million years ago, climate in Greenland resembled the forecast of a future under global warming: with trees such as poplars and birch and animals like hare, lemmings, mastodons and reindeer. Paleoclimatic records show strong polar amplification with annual temperatures of 11–19 degrees Celsius above current values. The biological communities inhabiting the Arctic…
Improving precision of pressure determination in nanosecond X-ray diffraction experiments
X-ray diffraction measurements under laser-driven dynamic compression allow researchers to investigate the atomic structure of matter at hundreds of thousands of atmospheres of pressure and temperatures of thousands of degrees, with broad implications for condensed matter physics, planetary science and astronomy. Pressure determination in these experiments often relies on…
W87-1 The Modification that Invigorated an Enterprise
Lawrence Livermore will deliver the first newly manufactured nuclear warhead in three decades, which will replace the aging W78, meet military requirements, improve safety and security, and transform the Nuclear Security Enterprise through innovative collaborations.
Iron under Extremes
Lawrence Livermore scientists have performed a series of experiments through the National Ignition Facility’s (NIF’s) Discovery Science Program to replicate the extreme conditions within super-Earth cores and answered many questions posited by theoretical predictions and extrapolations from previously established relatively low pressure–temperature experimental data.
LLNL Forensic Science Center team develops new technique to analyze fentanyl in blood and urine
A team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists has developed a new technique to analyze fentanyl in human blood and urine samples that could aid work in the fields of medicine and chemical forensics. Led by Carlos Valdez, an LLNL synthetic chemist and lead author, the team discussed its new fentanyl analysis approach in a paper recently published in the…
Machine-learning model instantly predicts polymer properties
Hundreds of millions of tons of polymer materials are produced globally for use in a vast and ever-growing application space with new material demands such as green chemistry polymers, consumer packaging, adhesives, automotive components, fabrics and solar cells. But discovering suitable polymer materials for use in these applications lies in accurately predicting the…
Honoring our veterans: Meet PLS’s James Jones
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) holds a quarterly Veterans Showcase to spotlight the work our veterans did while serving the nation and the work they continue to do in their Laboratory careers. The showcase held on November 9, 2022, highlighted the accomplishments of third-generation military veteran James Jones, who after joining the army at the age of 17,…
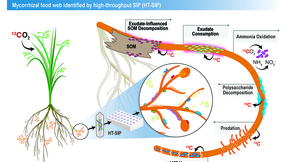
New method unearths improved understanding of soil microbial interactions
Linking the identity of wild microbes with their physiological traits and environmental functions is a key aim for environmental microbiologists. Of the techniques that strive for this goal, Stable Isotope Probing — SIP — is considered the most effective for studying active microorganisms in natural settings. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have…
Uranium takes an alternate pathway under extreme conditions
Under normal conditions, radioactive materials such as uranium work in a predictable manner. But take those same materials and put them under extreme conditions with high temperature in a short timescale and a rapid cooling process and their decomposition pathways change dramatically. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists built a unique process to…
LLNL celebrates 70 years of innovative science
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) held an Employee Engagement Day to celebrate the institution’s 70th anniversary on October 11, 2022. For the event, the Physical and Life Sciences (PLS) directorate hosted a variety of tours and activities, providing a behind-the-scenes look into our multidisciplinary research efforts. The Biosciences and Biotechnology Division…
New analysis helps reconcile differences between satellites and climate models
Satellite observations and computer simulations are important tools for understanding past changes in Earth’s climate and for projecting future changes. However, satellite observations consistently show less warming than climate model simulations from 1979 to the present, especially in the tropical troposphere (the lowest ~15km of Earth’s atmosphere). This difference has…
Scientists use carbon to detect a new nitrogen source in the open ocean
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and UC Santa Cruz scientists have detected a previously hypothesized class of nitrogen fixation in the surface ocean. Nitrogen scarcity limits the growth of ocean phytoplankton, a globally important carbon sink and the base of the marine food web. Nitrogen that can be used by phytoplankton generally has a very low concentration…
LLNL physicist probes causes of life-shortening 'dwell fatigue' in titanium
"Dwell fatigue" is a phenomenon that can occur in titanium alloys when held under stress, such as a jet engine's fan disc during takeoff. This peculiar failure mode can initiate microscopic cracks that drastically reduce a component's lifetime. The most widely used titanium alloy, Ti-6Al-4V, was not believed to exhibit dwell fatigue before the 2017 Air France Flight 066…
Lab researchers study Rift Valley fever virus
Immune responses could be supported by drugs to help people recover from brain infections caused by Rift Valley fever virus Research by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists suggests that immune responses could be bolstered by drugs to help people recover from brain infections caused by an emerging pathogen. The emerging pathogen studied by the team,…
Lab researchers elected Optica fellows
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists Félicie Albert and Craig Siders have been selected as fellows of Optica (formerly OSA). Fellows are selected based on several factors, including distinguished contributions to education, research, engineering, business and serving the optics and photonics community. Click here to see the entire Optica 2023 class…