Back
Physical and Life Sciences
Capturing microbes in soil and plants
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have developed a custom microscope to image microbes in soil and plants at the micrometer scale. Live imaging of microbes in soil would help scientists understand how soil microbial processes occur on the scale of micrometers, where microbial cells interact with minerals, organic matter, plant roots and other…
Nature paper chronicles how researchers achieved burning plasma regime for the first time in a laboratory experiment
After decades of fusion research, a burning plasma state was achieved on November 2020 and February 2021 at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Ignition Facility (NIF), the world’s most energetic laser. Obtaining a burning plasma is a critical step toward self-sustaining fusion energy. A burning plasma is one in which the fusion reactions themselves are the…
Two LLNL scientists honored as 2022 Oppenheimer Science and Energy Leadership fellows
The Oppenheimer Science and Energy Leadership Program (OSELP) has selected Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory computer scientist Kathryn Mohror and materials scientist T. Yong Han as 2022 fellows. Established in 2017, OSELP is a distinguished fellowship program that brings together exceptional leaders to explore the complexities, challenges and opportunities facing the…
Breaking down the barriers in all solid-state batteries
Solid electrolytes may overcome key technological hurdles associated with the narrow electrochemical and thermal stability of conventional lithium (Li)-ion and sodium (Na)-ion batteries. However, many solid electrolytes — ceramics in particular — also suffer from poor cycling issues and limitations in their ability to efficiently transport ions. These limitations often…
New environmentally friendly method to extract and separate rare-earth elements
A new method improves the extraction and separation of rare-earth elements—a group of 17 chemical elements critical for technologies such as smart phones and electric car batteries—from unconventional sources. New research led by scientists at Pennsylvania State University and LLNL demonstrates how a protein isolated from bacteria can provide a more environmentally…
Hoagland recognized by American Nuclear Society (ANS)
Dylan Hoagland (PHYS) has won the 2021 ANS Mark Mills award. This award is presented to the student author who submits the best original technical paper contributing to the advancement of science and engineering related to the atomic nucleus. Dylan’s paper, “Solution of the Neutron Transport Equation on Unstructured Grids Using the Parallel Block Jacobi-Integral Transport…
Multiscale simulations of metal additive manufacturing processes
Much of the latent promise of metal additive manufacturing (AM) rests in the potential for controlled creation of spatially tailored microstructures, designed to optimize key build-scale properties through systematic variation across a build. Component optimization possibilities and performance potential expand enormously when this becomes possible. However, the extreme…
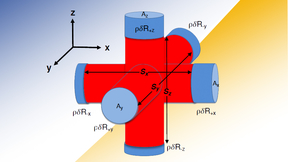
Research looks at ‘piston-model’ to understand impacts of asymmetry on ICF implosions
New research conducted at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) explores the expansion of a classical mechanics model, which has been useful for understanding asymmetries in inertial confinement fusion (ICF) implosions, from a two-piston to a six-piston model to capture higher-mode asymmetries. The work is featured in the Physics of Plasmas. LLNL authors included…
Lab researchers and collaborators to develop new vaccine against three biothreat pathogens
Scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and three other institutions are seeking to develop a multi-pathogen vaccine that will protect against three bacterial biothreat pathogens. Led by LLNL, the team includes disease experts from the University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center (UNMHSC), the University of Nevada, Reno School of Medicine (UNR Med)…
Ironing out the interiors of exoplanets
The discovery of more than 4,500 extra-solar planets has created a need for modelling their interior structure and dynamics. As it turns out, iron plays a key role. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and collaborators have used lasers at the National Ignition Facility to experimentally determine the high-pressure melting curve and structural…
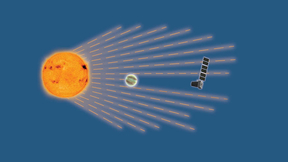
Pandora mission to study stars and exoplanets continues toward flight
The Pandora mission, co-led by a national laboratory and a NASA flight center, has passed a crucial step on its path to study stars and planets outside our solar system, or exoplanets. After a successful concept study report and system requirements review, NASA approved the mission to continue toward flight. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and NASA’s Goddard…
Unprecedented multiscale model of protein behavior linked to cancer-causing mutations
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers and a multi-institutional team of scientists have developed a highly detailed, machine learning-backed multiscale model revealing the importance of lipids to the signaling dynamics of RAS, a family of proteins whose mutations are linked to numerous cancers. Published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of…
LLNL scientist honored as 2022 American Astronomical Society fellow
LLNL physicist Richard Klein has been selected as a 2022 fellow of the American Astronomical Society. Klein, who was selected “for broad and influential contributions to computational astrophysics, for scientific achievements on radiatively-driven stellar winds and star formation theory and for training a generation of students and postdoctoral scholars,” is one of 23…
Fire may increase long-term carbon storage
Wildfires and prescribed burns, which can promote soil organic matter stability, may be an important nature-based climate solution to increase long-term carbon storage. That is the conclusion of an international team of researchers, including a scientist from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), who looked at the effect of wildfires and prescribed burns on the…
The Path to a Carbon Neutral California
A Livermore report outlines a strategy to reduce California’s carbon emissions to net zero by 2045.
A Shot Like No Other
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers aligned energetic materials knowledge and high-energy-density science expertise with experimental capabilities at the world’s most energetic laser, the National Ignition Facility.
Lost in space: Rocky planets formed from missing solar system material
By looking at the range of isotopic variations in terrestrial and meteoritic samples, a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist and collaborators have figured out that Earth and Mars formed by collisions of planetary embryos originating from the inner solar system. Rocky planets may have formed by two fundamentally different processes, but it is unclear…
Digital twins for cancer patients could be ‘paradigm shift’ for predictive oncology
A multi-institutional team, including a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) contributor, has proposed a framework for digital twin models of cancer patients that researchers say would create a “paradigm shift” for predictive oncology. Published online in Nature Medicine on Nov. 25, the proposed framework for Cancer Patient Digital Twins (CPDTs) — virtual…
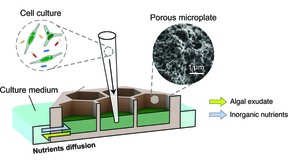
In the neighborhood of microalgae, location is key to bacterial carbon use
Microscopic algae are responsible for half of the global atmospheric carbon fixed from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, and may be used as a sustainable bioenergy source. The water immediately outside their cells, called the “phycosphere,” is rich with algal-excreted organic carbon, and is an ideal ecosystem for bacterial growth. However, detecting and measuring…
Microfabricated thin-film electrodes show therapeutic promise
Earlier this year, thin-film microgrid arrays developed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and used in neurologist Jon Kleen’s patients at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) showed that hippocampal brain activity consisted of waves that traveled bi-directionally during behavioral tasks. These thin-film microgrid arrays are designed not just to…