Back
Physical and Life Sciences
LLNL, other Bay Area labs to host webinar about business partnerships, the future of semiconductors
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and its three partner national labs in the Bay Area Lab Innovation Networking Center (LINC) will offer a webinar about the future of semiconductors and advanced materials on Wednesday, Aug. 25. The two-hour virtual Zoom webinar, called “Over the Horizon” and set to start at noon Pacific time, is primarily targeted at Bay Area…
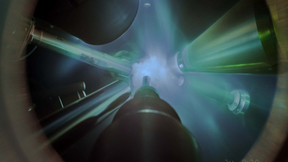
National Ignition Facility experiment puts researchers at threshold of fusion ignition
On Aug. 8, 2021, an experiment at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL’s) National Ignition Facility (NIF) made a significant step toward ignition, achieving a yield of more than 1.3 megajoules (MJ). This advancement puts researchers at the threshold of fusion ignition, an important goal of the NIF, and opens access to a new experimental regime. The experiment…
Researchers focus on how tantalum behaves at high pressure and temperature
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have explored high-pressure behavior of shock-compressed tantalum at the Omega Laser Facility at the University of Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE). The work showed tantalum did not follow the predicted phase changes at high pressure and instead maintained the body-centered cubic (BCC) phase until…
Simulating nuclear cloud rise anywhere, anytime
For decades, understanding the behavior of a nuclear mushroom cloud was done with careful analysis of observations made during the testing era. Old photos, outdated film and incomplete weather data made precise calculations difficult. Now, with results published in Atmospheric Environment, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists are improving our…
LLNL earn 'A' grade in OPCW biomedical proficiency test
It wasn’t an easy road, but Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) Forensic Science Center scientists earned an “A” grade in the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons’ (OPCW) recent biomedical proficiency test. In addition to the usual complexity of the sample preparations and analysis, the Livermore scientists received their proficiency test samples…
IPCC reports climate change is widespread, rapid and intensifying
Scientists are observing changes in the Earth’s climate in every region and across the whole climate system, according to the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Report, released today. Many of the observed climate changes are unprecedented in thousands, if not hundreds of thousands of years, and some of the changes already set in motion — such as…
LLNL's Forensic Science Center earns 'A' grade in OPCW environmental test
This fall, a score of scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's (LLNL) Forensic Science Center (FSC) will start two weeks of long days to undertake the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) environmental proficiency test. Livermore scientists have been taking the proficiency tests each October since 2001, with LLNL serving as one of two…
Planetary Research: Exploring Our Past and Future
How could life begin from a swirling chaos? How did Earth and its moon form? What can lunar rocks from the Apollo missions reveal? And what will scientists learn from exploration on distant moons? These questions are addressed in this four-part feature article on Lawrence Livermore’s space science research.
Three Decades of Explosive Innovation
Since Lawrence Livermore’s inception in 1952, Laboratory researchers have been among the nation’s leaders in understanding, synthesizing, formulating, testing, assessing, and modeling the initiation systems and energetic materials (EM) that play an integral role in the U.S. nuclear deterrent, conventional munitions, and homeland security. The Laboratory’s Energetic…
Embracing Risk for Transformational Results
Livermore researcher Sofia Quaglioni leads a project to develop methods for performing complex nuclear calculations on a prototype quantum computer.
Scientists use radiography to understand the evolution of liquid and solid microjets
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have experimentally tested the predictions of a 2020 study that computationally investigated the effect of melting on shock driven metal microjets. That earlier work predicted that melting the base material does not necessarily lead to a substantial increase in jet mass. The LLNL team confirmed the predictions of…
LLNL and collaborators improve electrochemical reactor performance through 3D printing
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and their collaborators are leveraging the power of 3D printing to improve the performance of electrochemical reactors used to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) to useful energy sources, chemicals and material feedstocks. Working under a cooperative research and development agreement (CRADA) with Stanford University and…
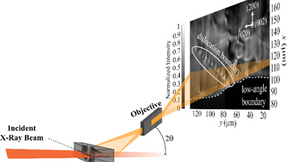
Watching subsurface defects as they move
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist and collaborators have demonstrated the first ever “defect microscope” that can track how populations of defects deep inside macroscopic materials move collectively. The research, appearing today in Science Advances, shows a classic example of a dislocation (line defect) boundary, then demonstrates how these same…
A few common bacterial groups gobble up the majority of carbon in soil
Just a few bacterial groups found in ecosystems across the planet are responsible for more than half of carbon cycling in soils, according to new findings from researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Northern Arizona University, published in Nature Communications. The new research suggests that despite the diversity of microbial taxa found in wild…
It’s no drag: New heavy vehicle design increases fuel efficiency, cuts carbon emissions
Reshaping the exterior of heavy vehicles, such as semitrucks, so that they are aerodynamically integrated along their entire length in a smooth, continuous fashion could reduce drag, increase fuel efficiency and cut carbon emissions. Using wind tunnel measurements and computational fluid dynamics simulations, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) engineers have…
Taking cues from nature, breakthrough ‘cellular fluidics’ technology could have sweeping impacts
Inspired by the way plants absorb and distribute water and nutrients, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have developed a groundbreaking method for transporting liquids and gases using 3D-printed lattice design and capillary action phenomena. In a paper published today in Nature and featured on the publication’s cover, LLNL researchers describe 3D…
LLNL’s Bill Pitz earns Department of Energy lifetime distinguished achievement award
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) engineer Bill Pitz has earned a lifetime distinguished achievement award from the Department of Energy’s Vehicle Technologies Office (DOE VTO) for his significant contributions to the field of chemical kinetics. Pitz, along with retiree Charles Westbrook, produced a chemical kinetic study of fuel additives for engine knock in…
Scientists create a novel instrument to probe thermal states of extreme matter on Earth
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have collaborated with Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) to design a novel X-ray crystal spectrometer to provide high-resolution measurements of a challenging feature of high energy density (HED) matter produced by National Ignition Facility (NIF) experiments. The work is featured in a paper in the Review…
LLNL/Tyvak space telescope goes into orbit
Thousands of images of Earth and space have been taken by a compact space imaging payload developed by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers and its collaborator Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems. Known as GEOStare2, the payload has two space telescopes that together have taken more than 4,500 pictures for space domain awareness, astronomy and Earth…
Research highlights techniques for studying materials under extreme conditions
The properties of materials under extreme conditions are of key interest to a number of fields, including planetary geophysics, materials science and inertial confinement fusion (ICF). In geophysics, the equation of state of planetary materials such as hydrogen and iron under ultrahigh pressure and density will provide a better understanding of their formation and interior…