Back
Physical and Life Sciences
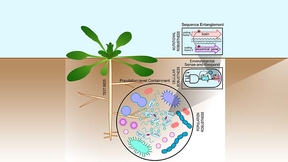
Building a secure biosystem to protect microorganisms
To reduce the risk of unintended ecological consequences from environmentally deployed, genetically engineered microorganisms (GEMS), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and collaborators are developing built-in “security mechanisms” that ensure they function where and when needed. The team hopes to stabilize GEMs to prevent the transfer of potentially…
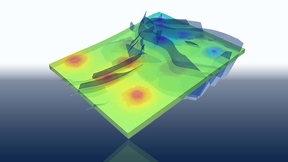
LLNL, partners open access to CO2 storage simulator
After more than two years of joint research, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Total and Stanford University are releasing an open-source, high-performance simulator for large-scale geological carbon dioxide (CO2) storage. The GEOSX simulator will enable researchers around the world to build on the work of the three partners, providing an open framework to…
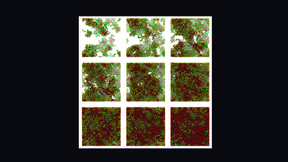
Lab explores new resins for light-based 3D printing
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has simulated the cross-linking of 3D-printed polymer networks, a key step toward developing new functional resins for light-based 3D-printing techniques including two-photon lithography (TPL) and volumetric additive manufacturing (VAM). The team used molecular dynamics simulations to study, at a microscopic level, the…
A PROMISE to trace the path of individual carbon atoms
Like water molecules in a river, soil carbon atoms are always in motion. To better understand this action, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and collaborators have created a new conceptual framework as well as a simulation model that traces the path of individual carbon atoms as they interact with the environment -- undergoing biochemical…
DOE awards $18 million to LaserNetUS consortium
LaserNetUS, a network of facilities operating ultra-powerful lasers including those at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), has received $18 million from the Department of Energy (DOE) for user support. Established in 2018 by DOE, LaserNetUS is organized and funded by DOE’s Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES). The new network was created to provide vastly…
New materials help expand volumetric 3D printing
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have adapted a new class of materials for their groundbreaking volumetric 3D printing method that produces objects nearly instantly, greatly expanding the range of material properties achievable with the technique. The class of materials adapted for volumetric 3D printing are called thiol-ene resins, and they can…
Girls persevere for STEM in virtual conference
More than 150 girls logged into their computers, excited to participate in the first-ever virtual San Joaquin Expanding Your Horizons (SJEYH) conference via Zoom last month. Now in its 28th year, SJEYH has a long history of inspiring young women and fostering awareness of careers in science, technology, engineering and math (STEM). The annual event normally draws more than…
Mapping ‘fossil water’ helps achieve sustainable groundwater management in California
Identifying the areas where paleowater or “fossil water” — water that recharged before the Holocene started 12,000 years ago — is pumped for drinking water supply helps managers decide whether groundwater can sustainably meet future demands. This type of groundwater recharged during rainy periods under cooler and wetter conditions that ended about 10,000 years ago. Since…
Lab researchers win R&D 100 award
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers are among the developers of the top 100 industrial inventions worldwide, winning an R&D 100 award at this year’s annual event. The trade journal R&D World Magazine announced the winners of the awards, often called the “Oscars of invention,” during a virtual event and on the magazine’s website. With this year…
Four LLNL scientists honored as APS fellows
Four Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have been selected as 2020 fellows of the American Physical Society (APS). The new fellows represent a selection of physics expertise, ranging from laser plasma physics to magnetic fusion plasmas, to theoretical and computational understanding of plasma interactions and soft X-ray and free electron laser…
Lab has ties to Nobel Prize winner Andrea Ghez
The 2020 Nobel Prize in physics has been awarded to Andrea Ghez of the University of California, Los Angeles, and Reinhard Genzel of the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, for their discovery of the black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. They share the award with Roger Penrose of Oxford University for his mathematical proof that black holes are…
Corona supercomputer gets funding for COVID-19 work
With funding from the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), chipmaker AMD and information technology company Supermicro have upgraded the supercomputing cluster Corona, providing additional resources to scientists for COVID-19 drug discovery and vaccine research. The recent addition of nearly 1,000 AMD…
Santer honored with geophysical union award
Renowned Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) atmospheric scientist Ben Santer has been honored with the American Geophysical Union’s (AGU) 2020 Bert Bolin Award. The Bolin award is presented annually and recognizes groundbreaking research or leadership in global environmental change through cross-disciplinary, interdisciplinary and trans-disciplinary research in…
LLNL team solves 100-year-old metallurgy puzzle
To solve a 100-year puzzle in metallurgy about why single crystals show staged hardening while others don’t, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists took it down to the atomistic level. The research appears in the Oct. 5 edition of Nature Materials. For millennia, humans have exploited the natural property of metals to become stronger or harden when…
Measuring electrical properties of methane hydrates leads to better understanding of gases in seafloors
Methane hydrate is a crystalline solid formed from methane gas and water that occurs naturally in the seafloor of the continental shelves worldwide. Hydrate is considered a source of natural gas, a natural hazard or a potential contributor to ocean acidification and climate change. Its presence lowers the electrical conductivity of the seafloor in comparison to hydrate…
LLNL researchers named to planetary science panels
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) geologist Lars Borg and physicist Megan Bruck Syal were named by the National Academies of Science to a pair of Planetary Science and Astrobiology Decadal Survey committees last week, Borg as a member of the survey’s steering committee and Syal as a member of the Small Solar System Bodies panel. Over the coming year, the two…
Going with the flow for water purification
Membrane separations have become critical to human existence, with no better example than water purification. As water scarcity becomes more common and communities start running out of cheap available water, they need to supplement their supplies with desalinated water from seawater and brackish water sources. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have…
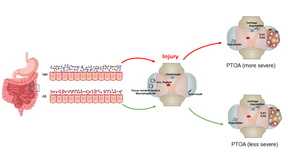
Antibiotic pre-treatment reduces joint inflammation
Tearing an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) can be an excruciatingly painful injury. Nearly 50 percent of these patients will develop a secondary form of osteoarthritis, deemed post-traumatic osteoarthritis (PTOA). Researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the UC Davis Medical Center have found that treatment with antibiotics prior to the injury…
A simple explanation to paradox of a spiraling football
The hallmark of a perfectly thrown football is a tight spiraling of the tip around the trajectory of the parabolic path of flight. Why the tip follows the trajectory has presented a paradox for some time. A team of researchers, including Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) physicist Willy Moss, provided a simple resolution to this paradox in a paper published as…
Inspiring future physicist while exploring dark energy
Doctoral student Victor Baules is spending his summer exploring the connection between dark energy and the expansion of our universe, but due to the pandemic, his research fellowship is more down-to-earth, taking place from his home in Alabama. Baules’ research trajectory in high-energy theory aligns with astrophysics research at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory …