Back
Physical and Life Sciences
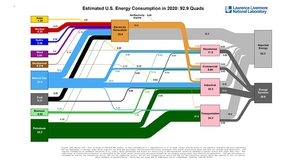
Pandemic drives down U.S. energy use in 2020
Americans used approximately 7 percent less energy in 2020, due in part to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to energy flow charts released by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). Each year, LLNL releases flow charts that illustrate the nation's consumption and use of energy. Americans used 92.9 quads (quadrillion BTU) of energy, which is 7.2 quads less or 7…
Researchers discover unusual property in hydrogen fuel device that could be ultimate guide to self-improvement
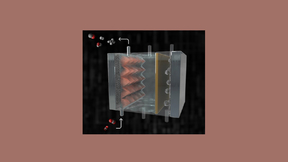
Three years ago, scientists at the University of Michigan discovered an artificial photosynthesis device made of silicon and gallium nitride (Si/GaN) that harnesses sunlight into carbon-free hydrogen for fuel cells with twice the efficiency and stability of some previous technologies. Now, scientists at Lawrence Livermore and Lawrence Berkeley national laboratories – in…
COVID-19 HPC Consortium reflects on past year
COVID-19 HPC Consortium scientists and stakeholders met virtually on March 23 to mark the consortium’s one-year anniversary, discussing the progress of research projects and the need to pursue a broader organization to mobilize supercomputing access for future crises. The White House announced the launch of the public-private consortium, which provides COVID-19 researchers…
Improved models of cloud drizzle-turbulence interactions could enhance future climate predictions
Large decks of closely spaced stratocumulus clouds hover over the ocean and cover vast areas — literally thousands of miles of the subtropical oceans — and linger for weeks to months. These marine clouds reflect more solar radiation than the surface of the ocean, providing a cooling effect on the Earth’s surface. Stratocumulus clouds are an important component of the Earth…
Researchers isolate geometric effects and resonant scattering in the X-ray spectra of HED plasmas
For the first time, researchers have isolated in a controlled laboratory setting the effects of the plasma geometry in its X-ray emission spectrum – the energy distribution of the radiation the plasmas emit. The work also is the first experimental testbed of the theories describing a phenomenon known in astrophysics as resonant scattering. This phenomenon is found in a…
Scientists put additive manufactured foams to the test
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists recently published the results of a three-week experimental campaign at the Lab’s Jupiter Laser Facility to test the performance of laser-heated additive manufactured foams. The project helps support two major Laboratory focus areas, including helping to advance additive manufacturing and by enabling improvements in…
HPCAT goes remote
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, HPCAT, a Chicago-based research consortium to advance high-pressure science in multidisciplinary fields using synchrotron radiation, hosted as many as 750 experimentalists each year—including numerous Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) teams. The consortium operates Sector 16 at the Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National…
Scientists put additive manufactured foams to the test
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists recently published the results of a three-week experimental campaign at the Lab’s Jupiter Laser Facility to test the performance of laser-heated additive manufactured foams. The project helps support two major Laboratory focus areas, including helping to advance additive manufacturing and by enabling improvements in…
Lab researchers find elevated CO2 emissions increase plant carbon uptake but decrease soil carbon storage
Elevated carbon dioxide emissions from human activities increase the uptake of carbon by plants but may decrease storage in soil. An international team led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists synthesized 108 elevated carbon dioxide (CO2) experiments in various ecosystems to find out how much carbon is absorbed by plants and soil. The research…
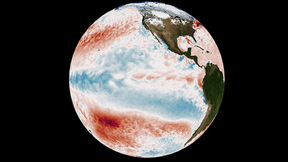
Natural variations help resolve a climate puzzle
New research shows that naturally occurring climate variations help to explain a long-standing difference between climate models and satellite observations of global warming. Satellite measurements of global-scale changes in atmospheric temperature began in late 1978 and continue to the present. Relative to most model simulations, satellite data has consistently shown less…
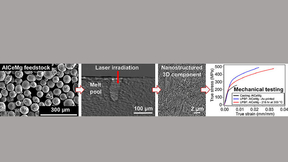
Enhancing the mechanical performance of aluminum alloys
Laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is a prominent additive manufacturing (AM) process that fuses thin layers of metal powder to underlying layers using laser melting in a sequential process. However, the high cooling rates and peak surface temperatures of the LPBF process can cause solidification defects in lightweight materials such as aluminum (Al) alloys, which have poor…
3D-printable gas diffusion layers promise improved performance in electrochemical reduction of CO2
Using carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions to create value-added products is an attractive approach to reduce net greenhouse gas emissions. Processes such as the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to ethylene and ethanol offer a pathway to producing commodity chemicals without fossil fuels when they are powered using low-carbon electricity. Gas diffusion electrode (GDE) assemblies…
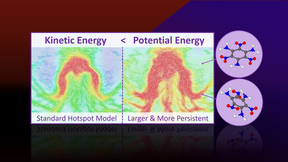
Research uncovers missing physics in explosive hotspots
Research conducted on Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) supercomputer Quartz highlights findings made by scientists that reveal a missing aspect of the physics of hotspots in TATB (1,3,5-trimamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene) and other explosives. Hotspots are localized regions of elevated temperature that form from shock-induced collapse of microstructural…
Greenland landscape history preserved under ice sheet
Greenland wasn’t always covered in ice. In fact, within the last 1.1 million years, Greenland had thriving vegetation and ecosystems. That is the conclusion of an international group of researchers, including a scientist from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), that analyzed sediment at the base of the Camp Century ice core (1.4 kilometers deep) collected in…
No miracles required: Scientists, industry experts agree California’s carbon capture and storage can be a reality
When it comes to California implementing a carbon capture and storage program to reach the state’s goal of carbon neutrality by 2045, nothing too newfangled needs to take place. During a forum titled “Carbon Capture and Sequestration in California: Regional Insights and Community Attitudes,” a group of scientists, California policymakers and industry leaders came together…
Stepped-up U.S. investment in fusion energy
An influential Department of Energy (DOE) advisory committee has recommended that the nation move aggressively toward the deployment of fusion energy, including investments in technology and equipment to support one of the core missions of LLNL’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) — laying the groundwork for the development of inertial fusion energy (IFE). The report,…
Ten-year anniversary of Fukushima observed
Ten years ago today, on March 11, 2011, a 9.0 Richter-scale earthquake and tsunami in Japan resulted in severe damage to the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant and also led to releases of radioactivity into the environment. That same day, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) activated Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Atmospheric Release Advisory Center …
Research identifies a pressure-induced increase in efficiency, phase transition of thermoelectric materials
Researchers have shown how applying pressure to a specific thermoelectric material, TiNiSn, increases its efficiency and leads to a structural phase transition. Thermoelectric materials are materials that can provide energy without the need for mechanical parts by converting heat energy into electrical energy. Thus, research aimed at these materials can identify new, more…
LLNL and NPS ink MOU for collaboration
Whether working informally or through a collaboration agreement, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the Monterey-based Naval Postgraduate School (NPS) have enjoyed an enduring relationship for more than two decades. While the two institutions have worked together informally for years, until recently they had only one memorandum of understanding (MOU)…
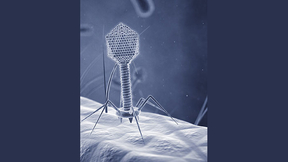
Fighting Bacterial Infections with Machine Learning
Scientists in the Forensic Science Center at Lawrence Livermore have partnered with San Diego State University and UCSD to advance bacteriophage therapy.