Back
Space
LLNL and Starris sign agreement, schedule conference talk for Aug. 13
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Starris: Optimax Space Systems have signed a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA), expanding production of LLNL’s next-generation space domain awareness technology. Starris will serve as the manufacturing partner that can scale production of monolithic telescope technology to meet the needs for…
LLNL selected by Defense Innovation Unit to build Pathfinder telescope for space vehicles
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has been selected by the U.S. Department of Defense’s Defense Innovation Unit (DIU) to provide a new monolithic telescope for a responsive space mission that will launch as early as 2027. Firefly Aerospace will host and operate the payload onboard its Elytra orbital vehicle during the mission in low Earth orbit (LEO), the area…
LLNL watch party shows off Rubin telescope’s first images
The NSF–DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory, a major new scientific facility jointly funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science, released its first imagery at an event in Washington, D.C., on June 23. The imagery shows cosmic phenomena captured at an unprecedented scale. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)…
Deep Purple payload successfully deployed and operational
The Deep Purple telescope developed by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers is now operational in space. The Livermore instrument, which utilizes a new design for an ultra-violet (UV) and short-wave infrared monolithic telescope features a novel, compact optical system and electronics package inside a lightweight, modular housing. On Friday, Aug. 16,…
Experiment sets new record in search for dark matter
Figuring out the nature of dark matter, the invisible substance that makes up most of the mass in our universe, is one of the greatest puzzles in physics. New results from the world’s most sensitive dark matter detector, LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ), have narrowed down possibilities for one of the leading dark matter candidates: weakly interacting massive particles, or WIMPs. LZ, led…
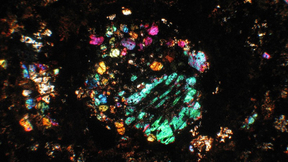
Unveiling Bennu asteroid samples
Now at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) lies a piece of ancient history. Very ancient history. The material, at just 120 milligrams, will provide information about the early solar system, planetary formation, and potentially, even ingredients for life on ancient Earth. LLNL scientists recently received and will analyze samples from the asteroid Bennu that will…
LLNL delivers compact dual-band telescope for launch this summer
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) space hardware team has delivered a payload for NASA’s Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator-R (PTD-R) satellite. LLNL developed the optical payload, called Deep Purple, that utilizes a new design for an ultra-violet (UV) and short-wave infrared (SWIR) monolithic telescope. The mission will demonstrate simultaneous monolithic UV…
LLNL gamma-ray sensor has the best resolution
It’s official. An instrument designed and built by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers is the highest-resolution gamma ray sensor that has ever flown in space. The Livermore high-purity germanium (HPGe) gamma ray sensor is an essential part of a larger gamma-ray spectrometer (GRS) built in collaboration with researchers from Johns Hopkins Applied…
Magnesium oxide undergoes dynamic transition when it comes to super-Earth exoplanets
Researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Johns Hopkins University have unlocked new secrets about the interiors of super-Earth exoplanets, potentially revolutionizing our understanding of these distant worlds. The focus of this work, magnesium oxide (MgO), a crucial component of Earth’s lower mantle, is believed to play a similar role in the…
Lab to provide optical payload for upcoming U.S. Space Force mission
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) Space Program is now building an optical space domain awareness payload for an upcoming mission by the U.S. Space Force. The planned mission, known as VICTUS HAZE, will be a tactically responsive space mission to demonstrate the ability to rapidly characterize an on-orbit threat. The U.S. Space Force selected Long Beach,…
LLNL Pandora SmallSat mission clears major NASA milestone on the path toward launch
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) Pandora SmallSat mission recently passed NASA’s critical design review: a major milestone for the mission to continue its journey toward launch. The Pandora SmallSat mission will study planets beyond our solar system, known as exoplanets, and their stars. “This is a major milestone for the mission and a huge accomplishment…
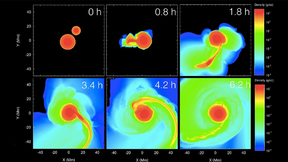
Using NIF to study the sluggish pace of star formation
Editor’s note: The principal mission of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) is to support the National Nuclear Security Administration’s science-based Stockpile Stewardship Program — and with the achievement of fusion ignition in 2022 at NIF, LLNL is further exploring the possible use of nuclear fusion as a future energy source…
Resolving astronomical mysteries
A new satellite called XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission, pronounced “crism”) was successfully launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan on Sep. 7, 2023. XRISM is a collaboration between the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), with European Space Agency participation, to study extreme…
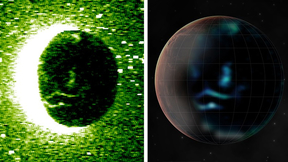
Lawrence Livermore optics used to spot elusive aurora on Red Planet
The United Arab Emirates' (UAE) Mars mission that launched about a year ago has recently captured the most detailed images of auroras in the Martian sky. The optics used to capture these images include a silicon carbide-coated mirror and diffraction grating for the Emirates Mars Ultraviolet Spectrometer (EMUS) that were developed by researchers at Lawrence Livermore…
Lab launches interdisciplinary Space Science Institute
What are the next world-class, game-changing concepts and technologies that will address the most important questions in astrophysics or planetary science? Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers will soon be better equipped to answer this question with the launch this month of a new Space Science Institute (SSI), intended to boost cross-discipline…
Kepler, don't give up on the hunt for exomoons
The Kepler spacecraft has been prolific in its search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets, discovering thousands since its launch in 2009. But the hunt for moons orbiting these exoplanets, or exomoons, is vastly more challenging. While no exomoons have been found to date, a new study shows that the search is not futile. Researchers have demonstrated…
Laboratory researchers find Earth composed of different materials than primitive meteorites
Scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have found that, contrary to popular belief, the Earth is not comprised of the same material found in primitive meteorites (also known as chondrites). This is based on the determination that the abundance of several neodymium (Nd) isotopes are different in the Earth and in chondritic meteorites. A long-standing…
Team tracks core of massive object in universe
International scientists have identified the dynamics of the core of one of the most massive objects in the known universe, bringing insight into the cosmology of clusters of galaxies. The Hitomi collaboration, in which Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientist Greg Brown is a member, found that the turbulent motion of the intracluster gas in the Perseus cluster is…
LLNL researchers garner two contracts for rocket propulsion, space launch vehicle work
Two recent contracts worth nearly $1.5 million have brought the Laboratory back into the rocket development business.The last Livermore designed and fabricated rocket vehicle, powered by an LLNL engine, was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base in 1994. It was conceived and designed by aerospace engineer John Whitehead and his team, which included collaborators from…
NASA taps Livermore photon scientists for heat-shield research
Researchers in Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's NIF & Photon Science Directorate are working with NASA Ames Research Center at Moffet Field, California on the development of technology to simulate re-entry effects on the heat shield for the Orion spacecraft, NASA's next crewed spaceship. Orion is designed to carry astronauts beyond low Earth orbit to deep-space…