Back
Physical and Life Sciences
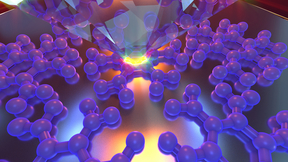
Precision fabrication of gold nanowires
A new generation of ultra-low-density (less than 20 milligrams per cubic centimeter) metal foams for laser targets has been made from metal nanowire suspensions via a unique freeze-casting process. In order to optimize the density, geometry, composition, and mechanical properties of these metal foams, it is necessary to develop nanowire stock materials of highly controlled…
Describing plutonium from first-principles theory
A new publication in the journal Advances in Physics by three Laboratory researchers describes plutonium from first-principles theory. This is the first time a first-principles explanation for the perplexing anomalous negative thermal expansion of the delta phase of plutonium has been reported. Per Söderlind, Alex Landa, and Babak Sadigh (all PHYS) reviewed developments in…
Shedding light on electron–laser interactions
When an electron encounters a laser pulse, it “wiggles” and radiates electromagnetic waves. As simple as this may sound, scientists have long struggled with an unresolved question: is the radiation energy provided by the laser or the electron? At low laser intensity, it has been experimentally confirmed that the radiation energy is entirely provided by the laser, while at…
Multilayer coatings for hard x rays
Multilayer interference mirrors are enabling components in x-ray optical systems. These mirrors consist of periodic or non-periodic structures of alternating thin film layers of two or more materials deposited on an optical substrate. Today’s applications and experimental facilities (including the National Ignition Facility) require novel, multilayer-based hard x-ray…
Researchers dish the dirt on soil microbes
Soil microbes are wild, unpampered and uncultured. But to understand their ecology, don't look in laboratory cultures, look in the soil. That’s exactly what Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Northern Arizona University (NAU) scientists did. Relationships between microbial genes and performance are often evaluated in the lab in pure cultures, with little…
Detection array wins FLC national award
In the nine years since a virtually all-encompassing Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) biological detection system was first introduced, it has become a major hit among technologies. Now called the Applied Biosystems’™ Axiom™ Microbiome Array (ABAMA), the biological detection technology has attracted more than 30 collaborators, has advanced into the marketplace…
Researchers discover an unexpected phase transition in the high explosive TATB
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists in collaboration with University of Nevada Las Vegas (UNLV) have discovered a previously unknown pressure induced phase transition for TATB that can help predict detonation performance and safety of the explosive. The research appears in the May 13 online edition of the Applied Physics Letters and it is highlighted…
Sustained nuclear fusion in the Z pinch concept
Controlling nuclear fusion for power production is expected to require large and expensive magnetic coils or laser systems to create, heat, confine, and control the hot plasma needed to sustain fusion reactions. The idea of directly driving a column of plasma with an electrical discharge, known as Z pinch, was a simple and early method envisioned as a possible path to…
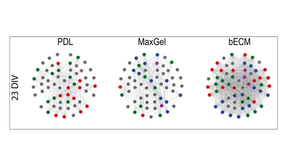
Understanding effects of tissue-specific extracellular matrix molecules on brain cells
In vitro organ-on-a-chip experimental platforms hold great promise to predict human biology and human-relevant responses to chemical and biological stimuli. LLNL scientists and engineers are working to more faithfully recapitulate the brain microenvironment on multi-electrode arrays to study brain activity. In an article recently published in Scientific Reports, Livermore…
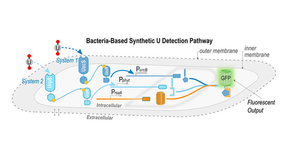
Designing sensors for environmental uranium detection
The ability to detect uranium (U) through environmental monitoring is of critical importance for informing water resource protection and nonproliferation efforts. While technologies exist for environmental U detection, wide-area environmental monitoring—sampling coverage over large areas not known to possess U contamination—remains a challenging prospect that necessitates…
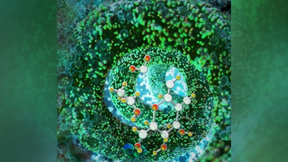
Bioprinting of live cells enhances catalytic efficiency
Critical to the success of high-performance, three-dimensional (3D) printed living materials is the development of new ink materials and 3D geometries that favor long-term cell functionality. To address this challenge, a cross-directorate LLNL team, collaborating with National Renewable Energy Laboratory researchers, has invented a new bio-ink system using viable freeze…
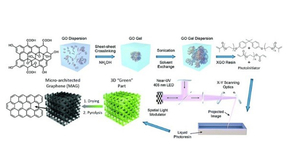
Additive manufacturing paper makes waves
An article entitled “Additive Manufacturing of Complex Micro-Architected Graphene Aerogels” (doi: 10.1039/c8mh00668g) is featured among the most popular articles published by Materials Horizons in 2018. Materials Horizons is positioned as “the new home for rapid reports of exceptional significance on innovative materials.” The paper describes the fabrication of architected…
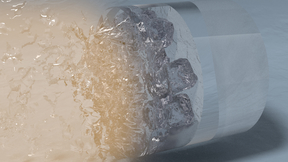
Giant lasers crystallize water with shockwaves, revealing the atomic structure of superionic ice
Scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) used giant lasers to flash-freeze water into its exotic superionic phase and record X-ray diffraction patterns to identify its atomic structure for the very first time — all in just a few billionths of a second. The findings are reported today in Nature. In 1988, scientists first predicted that water would…
"Mini" Device Set to Analyze Mysterious Psyche
As part of a NASA Discovery Program mission, an LLNL researcher is leading a team to develop an instrument for analyzing Psyche’s composition.
Human impact on droughts goes back 100 years
Observations and climate reconstructions using data from tree rings confirm that human activity was affecting the worldwide drought risk as far back as the early 20th century. New research from NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Columbia University shows that greenhouse gas emissions in the first half of the…
U.S. energy use rises to highest level ever
Americans used more energy in 2018 than in any other year, according to the most recent energy flow charts released by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). Overall total energy consumption rose to 101.2 quadrillion BTU (or "quads"). The prior record, set in 2007, was 101.0 quads. Energy use went up by 3.6 percent from 2017, which also is the largest annual…
Belof elected Kavli Fellow of the National Academy of Sciences
Jon Belof, a group leader in MSD and a physicist at LLNL since 2010, has been elected a Kavli Fellow of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences (NAS). As a recently elected fellow, Jon was invited to attend the NAS Frontiers of Science symposium in Irvine, California, the academy’s premiere activity for distinguished young scientists. Here, he presented his research on non…
Barrier membrane demonstrates biosensing platform protection
Biological signaling mechanisms often involve small molecules, ions, and protons, and facile in situ monitoring of the levels of these species is vital for medical diagnostics. Even the simplest signals, such as intracellular pH level, can provide important information. Of all biosensing platforms, electrical sensors represent the best opportunity to develop implantable…
Computational and Experimental Models Combine in Science on Saturday Program
LLNL scientists Nick Be (left) and Tim Carpenter describe the computational (in silico) methods and experimental (in vitro and in vivo) techniques used to speed up the therapeutic drug optimization process. The combination of these methods creates a pipeline to help scientists test more therapeutics at a lower cost. (Photo by Joanna Albala/LLNL Science Education Program.)…
Lab scientists use radioactive tracers to determine the ages of streamflow
Watersheds store water underground in soils and weathered bedrock. How long it takes for water to flow through the subsurface to feed streams is difficult to measure but important for understanding how watersheds function. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers and their collaborators have studied the mixture of water ages in Providence Creek, a stream…