Back
Physical and Life Sciences
Don't rule out severe global climate change yet
A key metric of global warming is the Earth’s "equilibrium climate sensitivity" (ECS), which represents the global surface warming that will accompany a doubling of atmospheric carbon dioxide. For nearly four decades, ECS was thought to be somewhere between 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit (F) and 8.1 degrees F, but a more precise estimate has eluded climate scientists. That was…
Oh what a mysterious web they weave
Spider silk is one of the strongest and most complex fibers in the world, but also remains one of nature’s mysteries. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researcher John Roehling and collaborators discovered that silk proteins inside spider glands are assembled in nanostructures and lend clues to how the silk is actually produced. The findings could be used to…
DOE looks to Jupiter for high-intensity research
The Department of Energy deemed Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) as one of nine facilities operating high-intensity, ultrafast lasers. DOE’s Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES) within the Office of Science awarded the new research network, called LaserNetUS, $6.8 million over the next two years. LaserNetUS includes the most powerful lasers in the United…
'Zombie' stars return from the dead
Black holes are among the most elusive objects in the universe, but research out of Lawrence Livermore National Labroatory (LLNL) suggests the remnant cores of burned-out stars could be the key to making the first observation of the most elusive class of black holes. The research explored whether a dormant white dwarf star — sometimes referred to as a "zombie" star — could…
Nanocrystals arrange to improve electronics
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers are working to make better electronic devices by delving into the way nanocrystals are arranged inside of them. Nanocrystals are promising building blocks for new and improved electronic devices, due to their size-tunable properties and ability to integrate into devices at low-cost. While the structure of…
LLNL researchers identify how many cancer cells it takes to initiate metastatic tumors
For the first time, researchers have developed a way to determine how many cancer cells it takes to initiate a tumor in another part of the body. The findings, made by a team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists, are published in the journal, Scientific Reports. "We think this is an exciting area of research," said LLNL biologist Nicholas Hum, the…
Big results come from small instrument
A new kid is coming to town in the form of an ultra-sensitive, laser-based, carbon-14 spectrometer that will be able to measure samples as small as one microgram of carbon. LLNL engineer Daniel McCartt has built laser-based detection methods for rare isotopes to supplement the Lab’s accelerator mass spectroscopy (AMS) detection capabilities. The new laser-based, rare…
Lab researchers named optical society fellows
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers Jay Dawson and Tayyab Suratwala have been named Fellows by The Optical Society of America (OSA), a distinction awarded to OSA members for their significant contributions to the advancement of optics and photonics. Dawson was cited for "leadership, innovations and contributions to the understanding of fiber laser…
Four Lawrence Livermore researchers named 2018 fellows of the American Physical Society
Four Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have been selected as 2018 fellows of the American Physical Society (APS). The new fellows represent a selection of physics expertise, ranging from computational physics to shock compression of condensed matter and instrument and measurement science. APS fellowships are awarded after extensive review and are…
New understanding of the solidification of high-pressure ice found in 'ocean world' planets
A team of theorists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has solved a long-standing puzzle in the nucleation of a high-pressure phase of ice known as ice VII, which is believed to exist near the core of "ocean world" planets recently detected outside of the solar system, and has recently been discovered to exist within the Earth’s mantle. The findings are…
New Consortium Aims to Expand HED Science Education and Research Collaborations
A three-year funding award from NNSA’s Minority Serving Institution Partnership Program enabled LLNL and three academic institutions to form the Consortium for High Energy Density Science, a partnership that aims to expand educational opportunities for students and research collaborations among the participating institutions, which include Florida A&M University,…
First experiments at Europe's new X-ray laser reveal unknown structure of antibiotics killer
DESY-led international collaboration obtains the first scientific results from European XFEL An international collaboration led by Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (DESY) and consisting of more than 100 researchers, including three Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists, has announced the results of the first scientific experiments at Europe's new X-ray…
LLNL Partners with UC San Diego and Other Institutions to Form an NNSA Center of Excellence
LLNL will be part of a new National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) Center of Excellence, which will be managed by the University of California (UC) San Diego. With funding provided by NNSA, the Center for Matter under Extreme Conditions (CMEC) will facilitate interaction between national lab scientists and university leaders and provide opportunities for students…
Revitalized materials and chemistry internship wraps up successful summer
Each summer, hundreds of college students from around the country flock to the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) campus to participate in LLNL’s varied and unique internship opportunities. This year, Megan Freyman and Rene Mercado, both graduate students at the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC), joined 82 other students in one such opportunity—a newly…
Research to focus on microbes in peat moss
Mention "peat moss" and many people will conjure up the curly brown plant material that gardeners use. "Oh, the thing you get at Home Depot" is a common reaction Joel Kostka receives when he mentions that he studies peat moss. His response: "Peat moss is a really cool plant that’s important to the global carbon cycle." The National Science Foundation has just awarded…
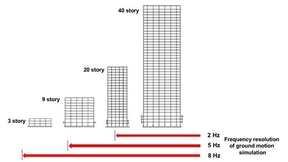
Using supercomputers to quantify Bay Area earthquake hazard and risk
With unprecedented resolution, Lawrence Livermore and Lawrence Berkeley national laboratory scientists and engineers are simulating precisely how a large-magnitude earthquake along the Hayward Fault would affect different locations and buildings across the San Francisco Bay Area. The researchers reported on their recent simulations in June at the U.S. National Conference…
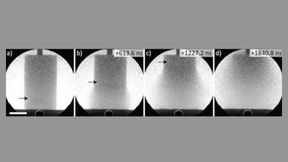
Imaging of detonation fronts using scattered synchrotron radiation
Many high explosives contain carbon, which condenses during detonation to produce nanometer-scale graphite and diamonds. These forms of carbon and their particle growth reaction rates are neither well known nor easily measured because the optical opacity at the detonation front has, until now, hindered the measurement and study of detonation phenomena at nanoscale time and…
Reviewing the evolution and application of kinetic reaction mechanisms
When researchers use kinetics to understand and predict the chemical behavior of reactive systems, the basic tool connecting the kinetics and the reactive system is the reaction mechanism. The characteristics and capabilities of current kinetic reaction mechanisms are the product of a great deal of directed evolution, which is motivated by the need to be able to model the…
Journey to explore the inexhaustible resource of genetic information found in microorganisms
The microbial production of enzymes, chemicals and fuels could become more efficient and economical with a newly engineered system for controlling genes called "Jungle Express." Scientists and collaborators from the Department of Energy's (DOE) Joint BioEnergy Institute, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Lawrence Berkeley National Lab and San Francisco State…
HEDS Center Strategic Plan Emphasizes Education and Collaborative Research
LLNL’s High Energy Density Science (HEDS) Center released its five-year strategic plan in September 2018, highlighting the Center’s focus on fostering expanded research collaborations in the field of HED science and increasing the number of scientists working in this rapidly evolving discipline. The strategic planning group—led by HEDS Center Director Frank Graziani—met…