Back
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing
Big Data Illuminates the Physical Sciences
Astrophysics is a growth area in the Laboratory’s advancement of basic science for national and global security needs. In this field, data science helps researchers catalog and interpret objects orbiting Earth and process huge volumes of data captured by ground- and space-based telescopes.
Precision fabrication of gold nanowires
A new generation of ultra-low-density (less than 20 milligrams per cubic centimeter) metal foams for laser targets has been made from metal nanowire suspensions via a unique freeze-casting process. In order to optimize the density, geometry, composition, and mechanical properties of these metal foams, it is necessary to develop nanowire stock materials of highly controlled…
Describing plutonium from first-principles theory
A new publication in the journal Advances in Physics by three Laboratory researchers describes plutonium from first-principles theory. This is the first time a first-principles explanation for the perplexing anomalous negative thermal expansion of the delta phase of plutonium has been reported. Per Söderlind, Alex Landa, and Babak Sadigh (all PHYS) reviewed developments in…
Multilayer coatings for hard x rays
Multilayer interference mirrors are enabling components in x-ray optical systems. These mirrors consist of periodic or non-periodic structures of alternating thin film layers of two or more materials deposited on an optical substrate. Today’s applications and experimental facilities (including the National Ignition Facility) require novel, multilayer-based hard x-ray…
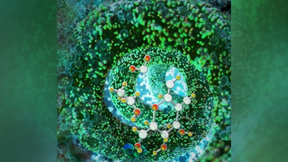
Bioprinting of live cells enhances catalytic efficiency
Critical to the success of high-performance, three-dimensional (3D) printed living materials is the development of new ink materials and 3D geometries that favor long-term cell functionality. To address this challenge, a cross-directorate LLNL team, collaborating with National Renewable Energy Laboratory researchers, has invented a new bio-ink system using viable freeze…
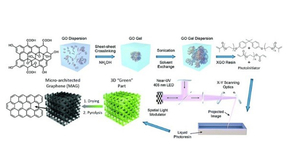
Additive manufacturing paper makes waves
An article entitled “Additive Manufacturing of Complex Micro-Architected Graphene Aerogels” (doi: 10.1039/c8mh00668g) is featured among the most popular articles published by Materials Horizons in 2018. Materials Horizons is positioned as “the new home for rapid reports of exceptional significance on innovative materials.” The paper describes the fabrication of architected…
Belof elected Kavli Fellow of the National Academy of Sciences
Jon Belof, a group leader in MSD and a physicist at LLNL since 2010, has been elected a Kavli Fellow of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences (NAS). As a recently elected fellow, Jon was invited to attend the NAS Frontiers of Science symposium in Irvine, California, the academy’s premiere activity for distinguished young scientists. Here, he presented his research on non…
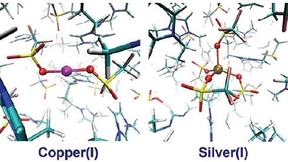
Metal ion solvation in ionic liquids
Understanding the behavior of metal ions in room temperature ionic liquids is essential for predicting and optimizing performance for technologies like metal electrodeposition. A recent paper by Livermore researchers describes a first-principles molecular dynamics simulations approach to understanding and comparing the key structural properties metal ions (Cu+ and Ag+) in…
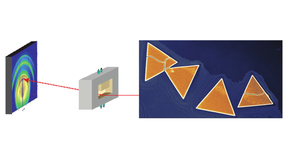
Better magnets from SmCo5 nanoparticles
A paper by Livermore researchers, in partnership with researchers at Brown University, has been designated a “hot paper” by the journal Angewandte Chemie. In this article, the authors describe a new technique to synthesize samarium-based nanomagnets and align them in a magnetic field to improve their performance. These show the highest saturation magnetization to date for…
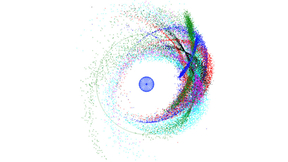
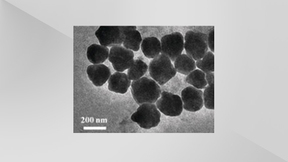
Probing silver nanocrystal superlattices
Typically, superlattices—faceted crystals composed of nanocrystal building blocks—have been made using slow evaporative techniques that often take days to weeks to form highly crystalline solids. This process is difficult to control, which has made it hard to systematically tune film properties and has hindered quantitative study of the assembly process. To overcome these…
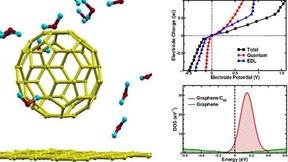
Next-generation graphene supercapacitors
Understanding and controlling the electrical response at a complex electrode–electrolyte interface is key to the development of next-generation supercapacitors and other electrochemical devices. While it is largely acknowledged that the capacitive performance of these devices is governed by both the quantum capacitance of the electrode and the electric double layer…
Revitalized materials and chemistry internship wraps up successful summer
Each summer, hundreds of college students from around the country flock to the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) campus to participate in LLNL’s varied and unique internship opportunities. This year, Megan Freyman and Rene Mercado, both graduate students at the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC), joined 82 other students in one such opportunity—a newly…
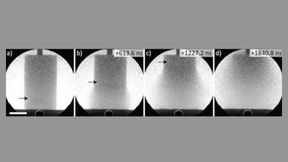
Imaging of detonation fronts using scattered synchrotron radiation
Many high explosives contain carbon, which condenses during detonation to produce nanometer-scale graphite and diamonds. These forms of carbon and their particle growth reaction rates are neither well known nor easily measured because the optical opacity at the detonation front has, until now, hindered the measurement and study of detonation phenomena at nanoscale time and…
Reviewing the evolution and application of kinetic reaction mechanisms
When researchers use kinetics to understand and predict the chemical behavior of reactive systems, the basic tool connecting the kinetics and the reactive system is the reaction mechanism. The characteristics and capabilities of current kinetic reaction mechanisms are the product of a great deal of directed evolution, which is motivated by the need to be able to model the…
Hierarchical 3D printing of nanoporous gold could 'revolutionize' electrochemical reactor design
Nanoporous metals are superior catalysts for chemical reactions due to their large surface area and high electrical conductivity, making them perfect candidates for applications such as electrochemical reactors, sensors and actuators. In a study published today in the journal Science Advances, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers, along with their…
Energy Secretary honors Lab scientist's contributions to stockpile stewardship
Secretary of Energy Rick Perry recognized Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) chemist Bill McLean with a Secretary’s Achievement Award Wednesday in recognition of "pioneering technical contributions that have led to significant advancements in science-based stockpile stewardship." The Secretary’s Honor Awards are bestowed on individuals who have a singular…
Five researchers named to '40 Under 40' list
Five Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers join an eclectic group of entrepreneurs, writers, executives, philanthropists and more on Diablo Magazine’s annual "40 Under 40" list, which recognizes young professionals in the East Bay who are leading the charge in their fields. Louisa Pickworth, an experimental physicist and group leader in the Physics…
LLNL and Virginia Tech researchers achieve more complex 3D-printed graphene aerogel
Graphene aerogel is lighter than air but as strong as steel, and it’s already proven useful in aerospace, energy storage and insulation. While there have been recent advances in 3D printing of the novel material, achieving complex structures has been elusive, hampering the unique material’s full potential. To date, 3D printing of graphene aerogel has been done using direct…
Warhead life extension passes key milestone
The program to extend the life of the W80 nuclear warhead recently achieved a significant milestone when the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) gave passing grades to the plans to refurbish certain components and the proposed approach to developing component cost estimates. Passing the milestone confirms that the life extension program (LEP), dubbed the W80-4…
LLNL joins effort to 3D print parts for U.S. Navy
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) are lending their expertise in metal additive manufacturing to a new collaboration aimed at 3D printing critical replacement parts for the U.S. Navy. The Office of Naval Research recently announced an award of $9 million to fund a collaboration led by GE Global Research and aimed at developing a rapid process for…