Back
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing
Lab team earns DOE Secretary Achievement Award
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory‘s (LLNL) "Getting to Neutral" Carbon Emissions Team has earned a Department of Energy (DOE) Secretary Achievement Award for its groundbreaking work on how California could reach the goal of becoming carbon neutral by 2045. Representing some of the highest internal, non-monetary recognition that DOE employees and contractors can…
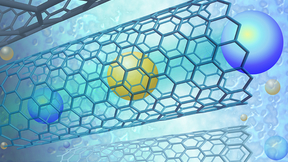
Fast transport in carbon nanotube membranes could advance human health
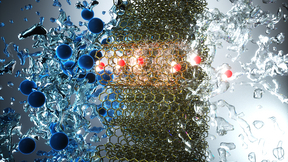
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have discovered that carbon nanotube membrane pores could enable ultra-rapid dialysis processes that would greatly reduce treatment time for hemodialysis patients. The ability to separate molecular constituents in complex solutions is crucial to many biological and man-made processes. One way is via the application…
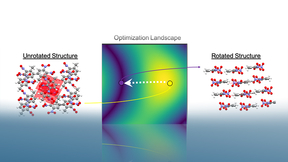
Molecular crystal structures pack it in
Whether organic chemists are working on developing new molecular energetics or creating new blockbuster drugs in the pharmaceutical industry, each is searching how to optimize the chemical structure of a molecule to attain desired target properties. Part of that optimization includes a molecular crystal’s packing motif, a perceived pattern in how molecules orient relative…
Lab garners five commercialization grants
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and engineers have put together another first-rate year securing major grants through the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Technology Commercialization Fund (TCF). “We did quite well, although the diversity of the research projects funded wasn’t as broad as last year,” said Rich Rankin, the director of the Lab’s…
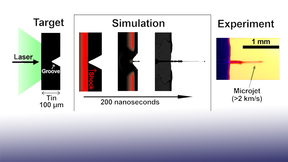
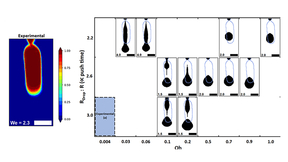
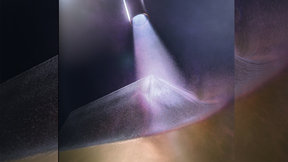
Microjets are faster than a speeding bullet
When a shock wave travels through material and reaches a free surface, chunks of material can break away and fly off at high speeds. If there are any defects on the surface, the shock forms microjets that travel faster than a speeding bullet. Understanding how these microjets form and how they interact with material help to improve spacecraft shielding and understanding a…
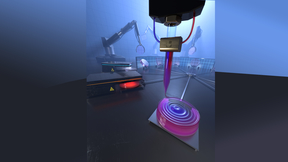
Lab study of droplet dynamics advances 3D printing
A team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists has simulated the droplet ejection process in an emerging metal 3D printing technique called “Liquid Metal Jetting” (LMJ), a critical aspect to the continued advancement of liquid metal printing technologies. In the paper, the team describes the simulating of metal droplets during LMJ, a novel process in…
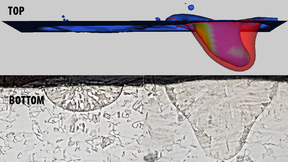
Researchers measure electron emission to improve understanding of laser-based metal 3D printing
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have taken a promising step in improving the reliability of laser-based metal 3D printing techniques by measuring the emission of electrons from the surface of stainless steel during laser processing. Researchers collected thermionic emission signals from 316L stainless steel under laser powder bed fusion (LPBF)…
Former LLNL intern makes history when she is named first Black woman to lead brigade at Naval Academy
Sydney Barber, former intern at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), is making history at the United States Naval Academy. It was recently announced that 1st class midshipman Barber will become brigade commander next semester, the highest leadership position in the brigade, making her the first Black woman to be named in the role. The first female brigade…
Lab scientists among most cited researchers worldwide
Fifty-seven researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) were among the top 2 percent of the most cited researchers worldwide throughout their careers, according to research on metascience by Stanford University. Metascience is the "study of studies" using scientific methods. Stanford University professor John Loannidis worked alongside U.S.-based Kevin…
3D printed electrodes free the gas
Alkaline water electrolysis has been touted as a path to establish a hydrogen economy by converting intermittent renewable energies into clean hydrogen-based chemical energy. However, current technology has achieved only low current densities and voltage efficiencies. To make electrolysis more resourceful, a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team partnered with…
3D-printed glass enhances optical design flexibility
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have used multi-material 3D printing to create tailored gradient refractive index glass optics that could make for better military specialized eyewear and virtual reality goggles. The new technique could achieve a variety of conventional and unconventional optical functions in a flat glass component (with no surface…
LLNL wins two FLC awards for tech transfer
Two teams of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and engineers, each supported by a Lab business development executive, have garnered regional awards for technology transfer. This year’s awards, one for outstanding technology development and the other for an outstanding partnership, will be presented next week during the Federal Laboratory Consortium’s…
Lab will play key role in upcoming battery summit
Five Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) employees, including Director Bill Goldstein, will play key roles in the sixth annual Bay Area Battery Summit (BABS) slated to be held virtually next week. This year’s sixth annual BABS, co-sponsored by LLNL, New Energy Nexus and CalCharge, will draw together investors, policymakers, researchers and entrepreneurs with an…
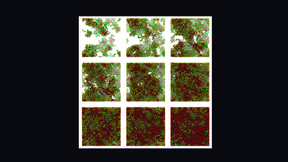
Lab explores new resins for light-based 3D printing
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has simulated the cross-linking of 3D-printed polymer networks, a key step toward developing new functional resins for light-based 3D-printing techniques including two-photon lithography (TPL) and volumetric additive manufacturing (VAM). The team used molecular dynamics simulations to study, at a microscopic level, the…
New materials help expand volumetric 3D printing
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have adapted a new class of materials for their groundbreaking volumetric 3D printing method that produces objects nearly instantly, greatly expanding the range of material properties achievable with the technique. The class of materials adapted for volumetric 3D printing are called thiol-ene resins, and they can…
Lab researchers win R&D 100 award
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers are among the developers of the top 100 industrial inventions worldwide, winning an R&D 100 award at this year’s annual event. The trade journal R&D World Magazine announced the winners of the awards, often called the “Oscars of invention,” during a virtual event and on the magazine’s website. With this year…
Four LLNL scientists honored as APS fellows
Four Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have been selected as 2020 fellows of the American Physical Society (APS). The new fellows represent a selection of physics expertise, ranging from laser plasma physics to magnetic fusion plasmas, to theoretical and computational understanding of plasma interactions and soft X-ray and free electron laser…
LLNL team solves 100-year-old metallurgy puzzle
To solve a 100-year puzzle in metallurgy about why single crystals show staged hardening while others don’t, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists took it down to the atomistic level. The research appears in the Oct. 5 edition of Nature Materials. For millennia, humans have exploited the natural property of metals to become stronger or harden when…
Measuring electrical properties of methane hydrates leads to better understanding of gases in seafloors
Methane hydrate is a crystalline solid formed from methane gas and water that occurs naturally in the seafloor of the continental shelves worldwide. Hydrate is considered a source of natural gas, a natural hazard or a potential contributor to ocean acidification and climate change. Its presence lowers the electrical conductivity of the seafloor in comparison to hydrate…
Going with the flow for water purification
Membrane separations have become critical to human existence, with no better example than water purification. As water scarcity becomes more common and communities start running out of cheap available water, they need to supplement their supplies with desalinated water from seawater and brackish water sources. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have…