Back
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing
Matter at extremes: a question of scale
Scaling laws are like a secret code used across science to break down complex phenomena into simple mathematical expressions. These equations help us to understand how one factor in a system relates to other factors that determine the system’s behavior. For example, Kleiber’s Law, one of the best-known scaling laws, observes that metabolic rates of many organisms — from…
New Lab projects to promote STEM diversity, accelerate battery research
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) will partner with outside institutions to improve diversity in the STEM workforce and provide training to underrepresented students and researchers under a pair of projects recently funded by the Department of Energy. With support from DOE’s Funding for Accelerated, Inclusive Research (FAIR) initiative, LLNL will partner with…
Understanding the plasticity of diamond for improved fusion ignition
Alex Li, a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) summer student in the Computational Chemistry and Materials Science Summer Institute, recently led a study published in the journal Matter to investigate the evolution of plasticity in diamond along different loading orientations and the effects that voids (pores) within the material can have on stresses within the…
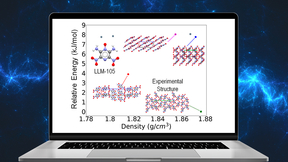
New research shows successful ab initio crystal structure prediction of energetic materials
New research by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers and collaborators from Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) demonstrates that crystal structure prediction is a useful tool for studying the various ways the molecules can pack together, also known as ubiquitous polymorphism, in energetic materials. The research also shows promise of becoming an integral part…
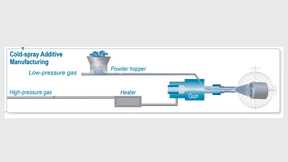
Versatile cold spray for a greener economy
Permanent magnets form the backbone of clean energy technologies from direct-drive wind turbines to electric motors, and will form a key component of the upcoming transition to a green economy. There is significant interest in the application of additive manufacturing approaches to produce permanent magnets, with techniques such as laser powder-bed fusion and binder-jet…
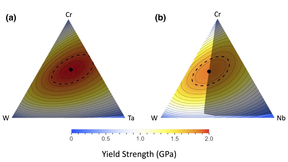
Designing materials for high-temperature structural applications
A materials science team, led by postdoctoral researcher Kate Elder, recently published a two-part series in npj Computational Materials. The research focuses on the computational discovery of ultra-strong, stable, and lightweight refractory metal-based multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs), which are compelling materials for high-temperature structural applications…
Georgia Tech duo spends summer at LLNL exploring materials processing and manufacturing
Professor Blair Brettmann from the Georgia Institute of Technology and her doctoral student Alexa Dobbs decided to spend a summer at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) to collaborate with the Lab’s materials science experts and learn more about LLNL’s experimental resources. During Brettmann’s faculty mini-sabbatical, she collaborated with researchers from LLNL…
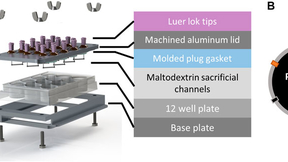
Platform tests colorectal cancer therapies in vitro
Colorectal cancer (CRC) — cancer of the colon or rectum — is the third-most common cancer in both men and women in the United States and the second-most common cause of cancer-related death in developed countries. Although surgery is highly successful for patients with a localized disease or disease confined to a narrow region (stages I–III), a total of 60% of CRC patients…
New composite may be key to improved hydrogen storage
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) computational scientists worked with experimental collaborators at Lawrence Berkeley and Sandia national laboratories to design metal amide-based composites capable of overcoming key kinetic limitations in their performance as hydrogen storage materials. Hydrogen possesses the highest energy density of any chemical fuel and can…
Explainable artificial intelligence can enhance scientific workflows
Machine learning techniques are increasingly being used in the sciences, as they can streamline work and improve efficiency. But these techniques are sometimes met with hesitation: When users don’t understand what’s going on behind the curtains, they may lack trust in the machine learning models. As these tools become more widespread, a team of researchers in Lawrence…
LLNL’s enhanced materials science capabilities showcased during open house
LLNL’s Materials Science Division (MSD) recently hosted an open house showcasing its lab facilities and redesigned workspaces that support the division’s expanding research scope. The event, led by Division Leader Manyalibo (Ibo) Matthews, featured tours of updated laboratory spaces. At each tour stop, MSD scientists provided a brief overview of the research that takes…
Machine learning reveals refreshing understanding of confined water
A new study provides surprising behavior of hydrogen bonding of water confined in carbon nanotubes. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists combined large-scale molecular dynamics simulations with machine learning interatomic potentials derived from first-principles calculations to examine the hydrogen bonding of water confined in carbon nanotubes (CNTs)…
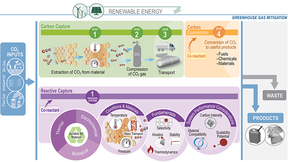
CO<sub>2</sub> capture and conversion perspectives for a cleaner future
To date, most CO2 capture and conversion processes have been developed in isolation, where the output of the capture process is purified, compressed CO2, which can be used as the feedstock for the CO2 conversion process. This is an energy intensive process and purified CO2 stream still needs to be delivered to the location where it will be converted to the desired product,…
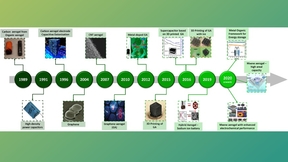
Energy storage for the future
The need for efficient and sustainable energy storage systems is becoming increasingly crucial as the world transitions toward renewable energy sources. However, traditional energy storage systems have limitations, such as high costs, limited durability, and low efficiency. Therefore, new and innovative materials and technologies, such as aerogels (highly porous networks…
Defense Programs Awards of Excellence recognize innovation and achievements in 2021
In virtual ceremonies held May 4 and June 26, Marvin Adams, deputy administrator for Defense Programs at the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), honored individuals and teams at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and partner sites for their outstanding contributions to nuclear security. The Defense Programs Awards of Excellence recognition events…
Advanced masking technology enables new applications for metasurface optics
Optics researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have refined their novel metasurface process to create taller features without increasing feature-to-feature spacing, an advance that unlocks exciting new design possibilities. “We have refined our process to create metasurfaces that allow for a wide optical bandwidth and a large span of incidence angles…
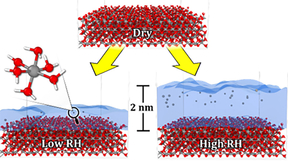
Research reveals how humidity affects atmospheric corrosion of aluminum metal
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) performed simulations using the Lab's supercomputer Ruby to uncover physical mechanisms that explain why humidity controls the rate of atmospheric corrosion of aluminum metal. Their research is featured in the ACS Journal of Applied Materials and Interfaces. Accurate predictions of aluminum component lifetimes…
Six Lab scientists partner with university researchers through WCI’s ACT Awards
Six scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory were recently granted awards through the Lab's 2022 Academic Collaboration Team (ACT) annual call for proposals. Now in their fourth year, ACT university collaboration awards were created to encourage and advance strategic partnerships among universities with a focus on the Lab’s and Weapons and Complex Integration’s…
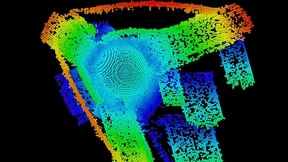
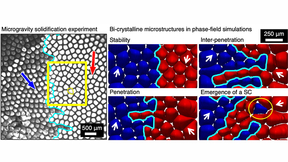
Microgravity experiments reveal metallurgical phenomena
In solidification processing, such as casting, welding, or additive manufacturing, cellular or dendritic patterns develop during the growth of a solid crystal from the liquid phase. In metallurgy, each similarly patterned region is referred to as a grain—which must be controlled during processing as grains affect structural performance. Additionally, the grain texture—the…
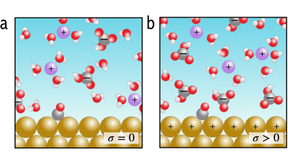
Microenvironment engineering for improved electrochemical reduction of CO<sub>2</sub>
Copper-based catalysts are highly active for electrochemical reduction of CO2 (CO2R) to several desirable hydrocarbon products, such as methane (CH4), formic acid (HCOOH), ethylene (C2H4), and ethanol (C2H5OH). CO2R is dually beneficial, as it allows for the conversion of excess atmospheric CO2 into useful chemicals. However, using copper-based catalysts for CO2R depends…