Back
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing
PLS postdocs battle it out at the 2021 Research Slam!
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL’s) fifth annual Research Slam! took place virtually on October 6th and featured 14 LLNL postdocs, 9 of which represented the Physical and Life Sciences Directorate (PLS). Over 300 people logged on to attend the live two-hour event, enthusiastically cheering for their favorite postdocs in the comment section. Each finalist was…
Lawrence Livermore Research Slam! winners advance to Bay Area competition
The top winners of the recent Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) Research Slam!, a speaking competition for postdocs, will advance to the Bay Area Research SLAM set for Thursday, Oct. 28. The Bay Area Research SLAM! is a collaboration between the Bay Area’s national labs (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, LLNL, Sandia National Laboratories and SLAC National…
At the extreme: Breaking the ice mold
New research involving Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists shows that water can remain liquid in a metastable state when transitioning from liquid to a dense form of ice at higher pressures than previously measured. Water at extreme conditions has attracted recent attention because of its complex phase diagram, including superionic ice phases having…
Researchers discover the first nerve-agent antidote that crosses the blood–brain barrier
A team led by LLNL scientists has discovered the first antidote against nerve-agent poisoning that crosses the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Their research, published in Scientific Reports, comes on the heels of a recent resurgence of nerve agents in transnational conflicts. Organophosphorus-based nerve agents (OPNAs)—including sarin, soman, and VX—cross the BBB and are…
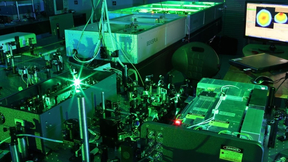
Researchers describe new technique to print transparent ceramics
In new research reported in Optics Letters and featured by the journal as an Editors’ Pick, LLNL researchers describe a new technique to print transparent ceramics with extremely fine feature sizes (in the tens of microns) for use as laser-amplification media. This technique is particularly amenable to thin film geometry and enables control of the composition and location…
LLNL, other Bay Area labs to host webinar about business partnerships, the future of semiconductors
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and its three partner national labs in the Bay Area Lab Innovation Networking Center (LINC) will offer a webinar about the future of semiconductors and advanced materials on Wednesday, Aug. 25. The two-hour virtual Zoom webinar, called “Over the Horizon” and set to start at noon Pacific time, is primarily targeted at Bay Area…
Planetary Research: Exploring Our Past and Future
How could life begin from a swirling chaos? How did Earth and its moon form? What can lunar rocks from the Apollo missions reveal? And what will scientists learn from exploration on distant moons? These questions are addressed in this four-part feature article on Lawrence Livermore’s space science research.
LLNL and collaborators improve electrochemical reactor performance through 3D printing
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and their collaborators are leveraging the power of 3D printing to improve the performance of electrochemical reactors used to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) to useful energy sources, chemicals and material feedstocks. Working under a cooperative research and development agreement (CRADA) with Stanford University and…
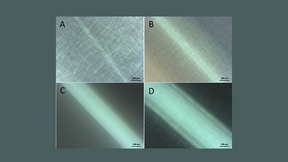
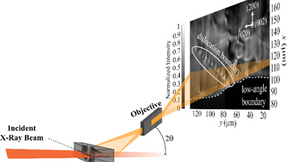
Watching subsurface defects as they move
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist and collaborators have demonstrated the first ever “defect microscope” that can track how populations of defects deep inside macroscopic materials move collectively. The research, appearing today in Science Advances, shows a classic example of a dislocation (line defect) boundary, then demonstrates how these same…
Taking cues from nature, breakthrough ‘cellular fluidics’ technology could have sweeping impacts
Inspired by the way plants absorb and distribute water and nutrients, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have developed a groundbreaking method for transporting liquids and gases using 3D-printed lattice design and capillary action phenomena. In a paper published today in Nature and featured on the publication’s cover, LLNL researchers describe 3D…
LLNL’s Bill Pitz earns Department of Energy lifetime distinguished achievement award
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) engineer Bill Pitz has earned a lifetime distinguished achievement award from the Department of Energy’s Vehicle Technologies Office (DOE VTO) for his significant contributions to the field of chemical kinetics. Pitz, along with retiree Charles Westbrook, produced a chemical kinetic study of fuel additives for engine knock in…
Machine learning aids in materials design
A long-held goal by chemists across many industries, including energy, pharmaceuticals, energetics, food additives and organic semiconductors, is to imagine the chemical structure of a new molecule and be able to predict how it will function for a desired application. In practice, this vision is difficult, often requiring extensive laboratory work to synthesize, isolate,…
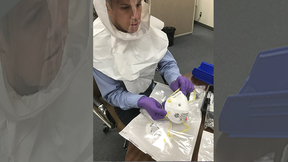
Decontaminating N95 masks for reuse
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have determined that heating N95 respirators up to 75 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes deactivates a surrogate coronavirus without compromising the device’s fit and its ability to filter airborne particles. This temperature (equivalent to 167 degrees Fahrenheit) is easily achieved in hospitals and field settings…
LLNL-patented power grid technology could reduce global CO2 emissions by 10 percent or more
To address inefficiencies in transmitting electricity over smart grids, engineers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and their collaborators have developed a light-activated switch that, if fully deployed, could reduce carbon emissions by more than 10 percent. Capable of sending high-voltage, direct-current power along grid lines and switching high voltages…
Lab’s Bill Pitz selected as SAE fellow
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) materials scientist Bill Pitz has been selected as a 2021 SAE fellow. Established in 1977, SAE fellow status is the highest grade of membership bestowed by the organization to members from industry and academia. More than 750 individuals have earned the distinction since its implementation. “I greatly appreciate being…
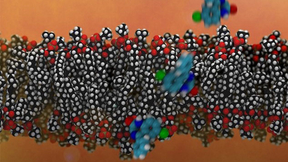
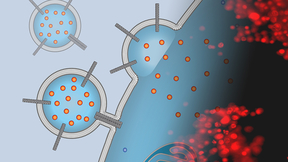
Direct drug delivery with carbon nanotube porins
Modern medicine relies on an extensive arsenal of drugs to combat deadly diseases such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, HIV-AIDS and malaria. Chemotherapy agents have prolonged lives for millions of cancer patients, and in some cases, cured the disease or turned it into a chronic condition. But getting those drugs into disease-ridden cells has remained a major challenge for…
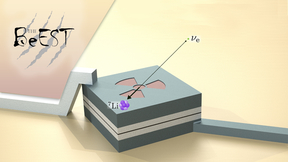
Sterile neutrinos may be portal to the dark side
“Sterile neutrinos” are theoretically predicted new particles that offer an intriguing possibility in the quest for understanding the dark matter in our universe. Unlike the known “active” neutrinos in the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics, these sterile neutrinos do not interact with normal matter as they move through space, making them very difficult to detect. A…
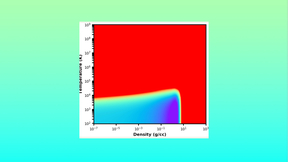
Researchers construct an EOS delivery paradigm for beryllium
Beryllium is a lightweight, low-density material used in a wide range of applications that require stability at high temperatures and pressures. Because of beryllium’s favorable traits, it has been considered as a potential capsule material for inertial confinement fusion (ICF) applications. Hydrodynamic simulations of ICF are frequently used to model the capsule behavior…
Researchers discover unusual property in hydrogen fuel device that could be ultimate guide to self-improvement
Three years ago, scientists at the University of Michigan discovered an artificial photosynthesis device made of silicon and gallium nitride (Si/GaN) that harnesses sunlight into carbon-free hydrogen for fuel cells with twice the efficiency and stability of some previous technologies. Now, scientists at Lawrence Livermore and Lawrence Berkeley national laboratories – in…
Scientists put additive manufactured foams to the test
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists recently published the results of a three-week experimental campaign at the Lab’s Jupiter Laser Facility to test the performance of laser-heated additive manufactured foams. The project helps support two major Laboratory focus areas, including helping to advance additive manufacturing and by enabling improvements in…