Back
Engineering
Open for business: NNSA, LLNL celebrate the dedication of new Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory
Officials from the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) gathered with elected leaders and industry professionals recently to dedicate and tour the Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory, a new collaborative hub intended to spur public-private partnerships. The $10 million, 14,000-square-foot facility, located in the…
Deep learning may provide solution for efficient charging, driving of autonomous electric vehicles
The future of commuter traffic probably looks something like this: ride-hailing companies operating fleets of autonomous electric vehicles alongside an increasing number of semi-autonomous EVs co-piloted by humans, all supported by a large infrastructure of charging stations. This scenario is particularly likely in California, which has committed to reducing carbon…
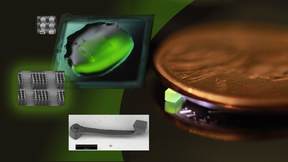
3D-printed aerogel electrodes boost energy storage
A team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and collaborators from the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) and Sun Yat-Sen University have developed a new class of aerogel electrodes with a simultaneous boost in energy and power density. The research could be a boon for the energy storage industry. “This is the first example in which we were…
Media advisory: LLNL, NNSA to dedicate new Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory
WHO: Leaders from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), industry partner representatives and Laboratory experts in advanced manufacturing and 3D printing. WHAT: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory will host a dedication ceremony and media tour of the Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory (AML), a state-of-the…
LLNL to receive DOE funding for new HPC4EI projects
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced the 12 projects awarded funding under the latest solicitation for the High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation Program (HPC4EI), a public/private collaboration that seeks to leverage DOE’s high performance computing facilities at national labs for industry to improve energy efficiency and streamline manufacturing…
LLNL team studies link between residual stress and mechanical properties of 3D-printed stainless steel
The buildup of microscopic residual stresses that occur during the process of 3D printing metal parts can lead to deformation and even cracking in the part, complicating the printing process and resulting in defects that cause damage and part failure. To develop a strategy for mitigating these tiny stresses, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have…
Lab team reports breakthrough in ultrafast, high-resolution nanoscale 3D printing
While 3D printing at the nanoscale — producing intricate features orders of magnitude smaller than the width of a human hair — has significant potential in industry and commercial applications, wide adoption has been impractical because of the slow speed and low throughput of the most widely used nanoprinting technique, two-photon lithography (TPL). But in the latest issue…
New 3D-printed lattice designs defy conventional wisdom on metamaterials
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have designed a new class of 3D-printed lattice structures that combine lightweight and high stiffness, despite breaking a rule previously thought to be required to exhibit such properties. One of the new structures additionally displays perfectly uniform response to forces in all directions. As described in a paper…
Students get a taste of Lab machinist work
Foothill High junior Lauren Graham has wanted to be an engineer since she took a class in eighth grade. Still undecided about her precise career path, she wants to expand her knowledge base and learn about all aspects of manufacturing. After seeing the many milling and welding machines, lathes and precision tools used at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), and…
New open-air facility will be testing ground for autonomous drones, vehicles and robots
The multicopter drone’s blades whirred, lifting it off the ground with a distinct hum, kicking up dust and propelling the craft through its preprogrammed flight path. The drone’s operators gazed at their laptop screens, closely monitoring the performance of the drone’s sensors while it carried out its maneuvers. Carrying a payload for the Department of Defense, the drone…
HPC4Manufacturing project aims at improving thin-film processes used in LED lights
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers are working with semiconductor chip manufacturer Applied Materials to improve a process for depositing thin-film materials on wafers that are used in high-efficiency LED lights and other products. The Department of Energy’s High Performance Computing for Manufacturing (HPC4Manufacturing) program is funding the…
HPC4Energy Innovation Program announces first awards for public/private partnerships
The High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation program (HPC4EI) today announced the nine public/private projects awarded more than $2 million from the Department of Energy (DOE), with aims of improving energy production, enhancing or developing new material properties and reducing energy usage in manufacturing. The projects represent the first joint round of funding…
New facilities to support stockpile stewardship
Leadership from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), Livermore Field Office (LFO) and contractor Hensel Phelps broke ground earlier this month on the Applied Materials and Engineering (AME) campus at LLNL. The groundbreaking was for the start of new building construction in the 2200 block of the Laboratory and…
High-powered laser diodes can reduce residual stress in metal 3D printed parts
In 3D printing, residual stress can build up in parts during the printing process due to the expansion of heated material and contraction of cold material, generating forces that can distort the part and cause cracks that can weaken or tear a part to pieces, especially in metals. Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the University of California,…
NFL comes to Lab to hear latest on TBI research
Officials from the National Football League visited Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) recently to hear how the Department of Energy’s (DOE) national laboratories are using high-performance computing and artificial intelligence to advance scientific understanding of traumatic brain injury (TBI). San Francisco 49ers chairman John York and NFL Executive Vice…
LLNL scientists use X-ray imaging, simulations to mitigate the defects in metal 3D-printed parts
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers, along with scientists at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory (SLAC), have discovered a solution to a major type of defect in metal 3D-printed parts. Combining high-performance computer simulations with X-ray imaging of the laser powder-bed fusion (LBPF) metal additive manufacturing process obtained with SLAC’s…
New call for HPC4EnergyInnovation proposals
The Department of Energy (DOE) and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) today announced the spring 2019 call for proposals for the High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) Program, including three of its pillar programs. Managed by LLNL in partnership with other national laboratories, the HPC4EI program aims to provide industry with HPC expertise…
HPC4Manufacturing Program names four awardees for latest round of DOE funding
The High Performance Computing for Manufacturing Program (HPC4Mfg) today announced the recipients of $1.2 million in federal funding for four public/private projects aimed at solving key manufacturing challenges in steelmaking and aluminum production through supercomputing. The summer 2018 HPC4Mfg call for proposals, the sixth overall for the program, had a special focus —…
LLNL/UCSF-developed implants enable unprecedented recordings of brain activity
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists, working with researchers at University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), have developed a novel system for recording widespread brain activity, using high-density implantable devices to collect real-time data over longer timescales and across multiple areas of the brain. The new platform, as recently reported in…
New multibeam metal 3D printer testbed to understand laser-material interactions
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and engineers have created the first research-grade, open-architecture multibeam metal 3D printer and are developing advanced diagnostics to understand the mechanics behind the multibeam process under a project funded by the Air Force Research Laboratory. To address the need for larger builds and faster print times,…