Back
Lasers and Optical S&T
Scientists develop a new geometry for a neutron source platform for NIF
The National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has added a new tool to its growing list of capabilities. A team of scientists has demonstrated a new geometry for a neutron source platform for NIF, called the inverted-corona platform, which does not rely on spherically symmetric laser irradiation. This new tool has significantly less…
How NIF inspired groundbreaking 3D metal-printing technology
A seminar at Stanford University, the decades-long quest for fusion energy and an innovative technique for protecting the National Ignition Facility's (NIF) optical components from laser damage were the inspiration for a new high-speed 3D manufacturing technology that’s about to enter the market. Developed by an industrial partnership between Lawrence Livermore National…
Scientists focus on cone targets to enhance temperature of electron beams
Intense short-pulse laser-driven production of bright high-energy sources, such as X-rays, neutrons and protons, has been shown to be an invaluable tool in the study of high energy density science. In an effort to address some of the most challenging applications, such as X-ray radiography of high areal density objects for industrial and national security applications,…
Scientists create a novel instrument to probe thermal states of extreme matter on Earth
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have collaborated with Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) to design a novel X-ray crystal spectrometer to provide high-resolution measurements of a challenging feature of high energy density (HED) matter produced by National Ignition Facility (NIF) experiments. The work is featured in a paper in the Review…
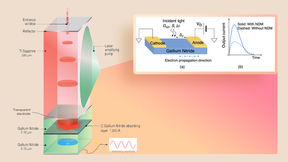
Lawrence Livermore team designs semiconductor switch for next-generation communications
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) engineers have designed a new kind of laser-driven semiconductor switch that can theoretically achieve higher speeds at higher voltages than existing photoconductive devices. The development of such a device could enable next-generation satellite communication systems capable of transferring more data at a faster rate, and over…
Research highlights techniques for studying materials under extreme conditions
The properties of materials under extreme conditions are of key interest to a number of fields, including planetary geophysics, materials science and inertial confinement fusion (ICF). In geophysics, the equation of state of planetary materials such as hydrogen and iron under ultrahigh pressure and density will provide a better understanding of their formation and interior…
From NIF to Z: LLNL continues to collaborate with Sandia on technology transfer projects
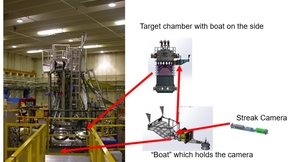
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Sandia National Laboratories continue to collaborate on diagnostic advancements on the nation’s premier high-energy density (HED) facilities. Mark Bowers, magnetic direct drive diagnostics manager at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), said current projects include providing NIF’s X-ray streak camera, neutron Time-of…
Smashing gold with finesse: Shockless compression experiments establish new pressure scales
To test the Standard Model of particle physics, scientists often collide particles using gigantic underground rings. In a similar fashion, high-pressure physicists compress materials to ever greater pressures to further test the quantum theory of condensed matter and challenge predictions made using the most powerful computers. Pressures exceeding 1 million atmospheres are…
Research describes slow and fast light in plasma
Slow and fast light, or large changes in the group velocity of light, have been observed in a range of optical media, but the fine control over the refractive index necessary to induce an observable effect has not been achieved in a plasma. In a paper published in Physical Review Letters, scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the Laboratory for…
Research describes slow and fast light in plasma
Slow and fast light, or large changes in the group velocity of light, have been observed in a range of optical media, but the fine control over the refractive index necessary to induce an observable effect has not been achieved in a plasma. In a paper published in Physical Review Letters, scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the Laboratory for…
Scientists use simulations to examine the performance of materials in NIF experiments
Scientists have examined the performance of pure boron, boron carbide, high-density carbon and boron nitride ablators — the material that surrounds a fusion fuel and couples with the laser or hohlraum radiation in an experiment — in the polar direct drive exploding pusher (PDXP) platform, which is used at the National Ignition Facility (NIF). The platform uses the polar…
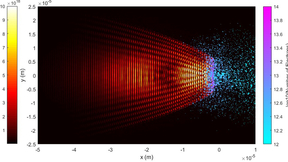
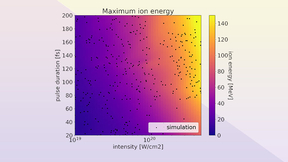
Laser-driven ion acceleration with deep learning
While advances in machine learning over the past decade have made significant impacts in applications such as image classification, natural language processing and pattern recognition, scientific endeavors have only just begun to leverage this technology. This is most notable in processing large quantities of data from experiments. Research conducted at Lawrence Livermore…
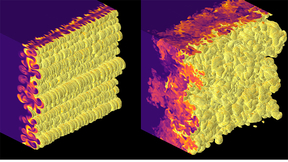
Scientists identify key trends in high-energy-density mixing layers
Imagine a bottle of salad dressing containing oil and vinegar. The oil has a lower density than vinegar, so it floats on the vinegar. The oil will not stay trapped under the vinegar if the bottle is flipped upside down. It will bubble up through the vinegar until a stable state is restored. This simple physical process is known as Rayleigh–Taylor instability, and it can be…
Scientists identify key trends in high-energy-density mixing layers
Imagine a bottle of salad dressing containing oil and vinegar. The oil has a lower density than vinegar, so it floats on the vinegar. The oil will not stay trapped under the vinegar if the bottle is flipped upside down. It will bubble up through the vinegar until a stable state is restored. This simple physical process is known as Rayleigh–Taylor instability, and it can be…
Students build knowledge of machinist trade during Lab's first-ever virtual Manufacturing Workshop
The COVID-19 pandemic didn’t prevent local high school students from learning what it’s like to be one of the more than 150 machinists who work at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) during the Materials Engineering Division’s (MED) Manufacturing Workshop, held April 20-22. Students attended the three-day workshop virtually after their school days ended, where…
Lawrence Livermore takes part in international planetary defense conference
Ten scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) last week took part in the 7th IAA Planetary Defense Conference (PDC), hosted by the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs in cooperation with the European Space Agency. Megan Bruck Syal, who helped lead the Lab’s participation in the event and who also was a conference session chair, said this year…
1D model helps clarify implosion performance at NIF
In inertial confinement fusion (ICF) experiments at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), a spherical shell of deuterium-tritium fuel is imploded in an attempt to reach the conditions needed for fusion, self-heating and eventual ignition. Since theory and simulations indicate that ignition efficacy in one-dimension (1D) improves with increasing imploded fuel convergence…
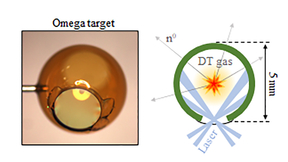
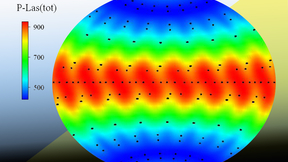
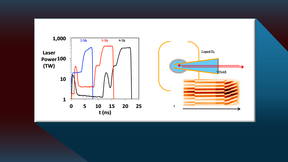
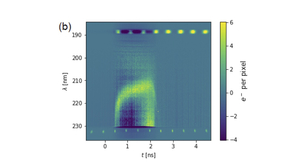
Team improves polar direct drive fusion neutron sources for use in National Ignition Facility experiments
Scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) are working to improve polar direct drive (PDD) neutron sources on the National Ignition Facility (NIF), the world’s most energetic laser. PDD neutron sources are capsules filled with deuterium-tritium (DT) gas at ambient temperature and shot with robust laser pulses…
Scientists reject restrictive heat flux models using directly driven gold spheres
A team of scientists have conducted an analysis of directly driven gold sphere experiments to test heat transport models used in inertial confinement fusion (ICF) and high energy density (HED) modeling. It was found that overly restricting the heat flux caused disagreement with measurement. However, simulations with a reduced nonlocal heat transport model quantitatively…
Lab team’s new interferometric instrument improves refractive index measurements at high pressure
In a paper recently published by Scientific Reports, a team of scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) describes a high-precision interferometer system, newly developed to measure the pressure dependence of the refractive index and its dispersion in diamond anvil cells (DACs). “Accurately measuring the index of a compressed sample in DACs is a…