Back
Physical and Life Sciences
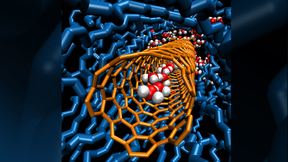
Tiny tubes move into the fast lane
For the first time, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have shown that carbon nanotubes as small as eight-tenths of a nanometer in diameter can transport protons faster than bulk water, by an order of magnitude.The research validates a 200-year old mechanism of proton transport.A nanometer is one billionth of a meter. By comparison, the diameter of a…
Reducing Reliance on Critical Materials
High-technology products, from car motors to fluorescent lighting, often rely on small amounts of scarce raw materials that possess key properties, such as strength, thermal resistivity, and magnetism.
Early and Mid-Career Scientists Recognized
Eight PLS researchers have been named to LLNL's second annual Early and Mid-Career Recognition (EMCR) Program. "Recognizing and encouraging early and mid-career technical staff is a key element in our strategy for retaining talent," Director Bill Goldstein said. "This program rewards employees at this stage in their careers who are exceptionally accomplished and show…
Scientists pump up batteries with metal oxides
Material scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have found certain metal oxides increase capacity and improve cycling performance in lithium-ion batteries.The team synthesized and compared the electrochemical performance of three graphene metal oxide nanocomposites and found that two of them greatly improved reversible lithium storage capacity.The research…
New gas-signature models can help inspectors locate and identify underground nuclear tests
Through experiments and computer models of gas releases, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists have simulated signatures of gases from underground nuclear explosions (UNEs) that may be carried by winds far from the point of detonation.The work will help international inspectors locate and identify a clandestine UNE site within a 1,000 square kilometer search…
Atmospheric carbon-14 measurements reveal natural production rate by cosmic rays
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have measured the carbon-14 isotope (14C) produced by cosmic rays in the stratosphere and found its production rate is less than most previous estimates.The team, led by Kristie Boering of the University of California, Berkeley and including Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists, measured the 14C content of…
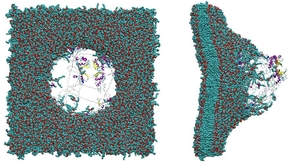
Shaving time to test antidotes for nerve agents
A simulation for drug-membrane permeability developed at LLNL increases the development speed for nerve-agent treatmentsImagine you wanted to know how much energy it took to bike up a mountain, but couldn’t finish the ride to the peak yourself. So, to get the total energy required, you and a team of friends strap energy meters to your bikes and ride the route in a relay,…
Lab researchers hunt for clues in transmission of deadly Middle Eastern respiratory virus
Lawrence Livermore Lab researchers have used new genetic sequencing technology and bioinformatics analysis to define how a novel and deadly respiratory virus changes when it passes from one host to another.The Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), an RNA virus related to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), can cause serious respiratory illness,…
Researcher sheds light on ocean observations
Oceanographer Paul Durack of the Laboratory’s Program for Climate Modeling and Intercomparison (PCMDI) recently opined about the importance of ocean salinity observations and needed urgent attention for the ocean observing system in the journal, Nature Climate Change. The global water cycle — where, when and how it rains, and the corresponding changes to water availability…
Scientist helps NASA develop medical device
In the future, NASA astronauts journeying into deep space may give themselves a health check-up with the aid of a small medical device developed by a team of scientists, including one from LLNL.Laboratory radiobiologist Matt Coleman is part of the six-scientist team, including researchers from NASA’s Ames Research Center, the University of California, Davis and Sandia…
Consequences of today's carbon emissions will linger for thousands of years, study finds
The Earth may suffer irreversible damage that could last tens of thousands of years because of the rate humans are emitting carbon into the atmosphere.In a new study in Nature Climate Change, researchers at Oregon State University, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and collaborating institutions found that the longer-term impacts of climate change go well past the…
Moniz awards Ian Hutcheon memorial fellowship
Energy Secretary Ernest Moniz last Thursday awarded the first Office of Defense Nuclear Nonproliferation (DNN) fellowship in honor of the late Ian Hutcheon, a longtime nuclear forensics expert at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, to Thomas Gray.Gray serves as a nonproliferation graduate fellow in the National Nuclear Security Administration’s Office of Defense…
Lab physicist awarded 2016 astrophysics prize by American Astronomical Society
The Laboratory Astrophysics Division of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) has selected LLNL researcher Peter Beiersdorfer as the recipient of the 2016 Laboratory Astrophysics Prize.This honor is given to an individual who has made significant contributions to laboratory astrophysics over an extended period of time. Beiersdorfer was cited for his numerous…
LLNL team demonstrates protein damage by shock waves in traumatic brain injury patients
New research by Lawrence Livermore scientists shows how shock waves can damage membrane proteins in traumatic brain injury patients.Blast-induced traumatic brain injury (TBI) from improvised explosive devices is the most frequent wound occurring from the conflicts in Afghanistan and Iraq. Estimates suggest more than 200,000 veterans have had at least one traumatic brain…
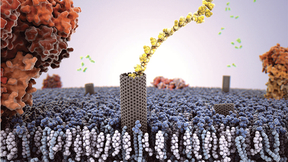
Researchers go for the gold on a single chip
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have created a library of nanoporous gold structures on a single chip that has direct applications for high-capacity lithium ion batteries as well as neural interfaces.Nanoporous gold (np-Au), a porous metal used in energy and biomedical research, is produced through an alloy corrosion process known as dealloying that…
Livermore scientists find global ocean warming has doubled in recent decades
LIVERMORE, California -- Lawrence Livermore scientists, working with National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and university colleagues, have found that half of the global ocean heat content increase since 1865 has occurred over the past two decades."In recent decades the ocean has continued to warm substantially, and with time the warming signal is reaching deeper…
Lawrence Livermore to work on DOE research program for electric grid modernization
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers will be working on 14 new grid research projects as part of the Grid Modernization Laboratory Consortium announced Thursday by Energy Secretary Ernest Moniz.Moniz released a blueprint for modernizing the grid, which is built on its Grid Modernization Initiative, an ongoing effort that reflects the Obama Administration’s…
Ask this chemist about creating new elements
Ever wonder how scientists create new elements, add them to the periodic table or why they’re even interested in super heavy elements?Dawn Shaughnessy, Lawrence Livermore’s principal investigator for the Heavy Element Group, will field questions from the public on the popular social media site Reddit from 10 a.m. to noon PST on Friday, Jan. 8.Shaughnessy is part of an…
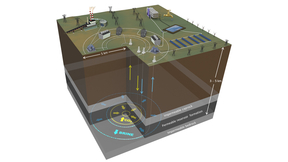
'Underground battery' could store energy, CO2
Meeting the Paris Climate Agreement goal of limiting the increase in the global average temperature to well below two degrees Celsius compared to pre-industrial levels will require increased use of renewable energy and reducing the CO2 intensity of fossil energy use.The intermittency of when the wind blows and when the sun shines is one of the biggest challenges impeding…
Lawrence Livermore credited with discovery of elements 115, 117 and 118
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has confirmed that Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists and international collaborators have officially discovered elements 115, 117 and 118.The announcement means those three elements are one step closer to being named.Lawrence Livermore teamed with the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in Dubna…