Back
Science
Livermore Lab Foundation, Lawrence Livermore National Lab launch carbon education and outreach program
Helping the general public and students learn about carbon neutrality, the options for carbon dioxide removal, as well as the effects of climate change, is the focus of the Carbon Cleanup Initiative, a unique public awareness partnership from the Livermore Lab Foundation (LLF) and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). “We are proud to partner with the scientists…
U.S. Department of Energy to showcase national lab expertise at SC21
The scientific computing and networking leadership of the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) national laboratories will be on display at SC21, the International Conference for High-Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis. The conference takes place Nov. 14-19 in St. Louis via a combination of on-site and online resources. The theme of this year’s…
LLNL-led team uses machine learning to derive black hole motion from gravitational waves
The announcement that the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) had detected gravitational waves during the merger of two black holes sent ripples throughout the scientific community in 2016. The earthshaking news not only confirmed one of Albert Einstein’s key predictions in his general theory of relativity, but also opened a door to a better…
Human-caused climate change increases wildfire activity
The western United States has experienced a rapid increase of fire weather as the vapor pressure deficit (VPD) increases in the area during the warm season. New research by scientists at University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) shows that two-thirds (approximately 68 percent) of the increase in VPD is due to human…
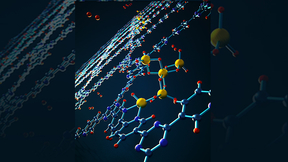
Disorder in surface materials key to better hydrogen storage
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have found that atomic disorder in certain boron-based hydrogen storage systems can potentially improve the rate of hydrogen uptake. Metal boride surfaces and their single-layer variants — known as borophenes — are generally thought to feature a regular arrangement of atoms at low to moderate temperatures. The LLNL…
Survivor salmon persist through drought and ocean warming
In drought years and when marine heat waves warm the Pacific Ocean, the rare late-migrating juvenile spring-run Chinook salmon of California’s Central Valley are the survivors. They are among the few salmon that return to spawning rivers in those difficult years to keep their populations alive, according to results published today in Nature Climate Change. The trouble is…
LLNL researchers garner three awards among top 100 industrial inventions
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and engineers have collected three awards among the top 100 industrial inventions worldwide. The trade journal R&D World Magazine announced the winners of the awards, often called the “Oscars of invention,” during a three-day virtual ceremony — Oct. 19-21 — and on the magazine’s website. With this year’s results,…
New hydrogen storage material steps on the gas
Hydrogen is increasingly viewed as essential to a sustainable world energy economy because it can store surplus renewable power, decarbonize transportation and serve as a zero-emission energy carrier. However, conventional high-pressure or cryogenic storage pose significant technical and engineering challenges. To overcome these challenges, Lawrence Livermore National…
Tube-in-tube structure going strong
Similar to grass stems, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have created nanostrut-connected tube-in-tubes that enable stronger low-density structural materials. Porous materials with engineered stretching-dominated lattice designs, which offer attractive mechanical properties with ultra-light weight and large surface area for wide-ranging applications…
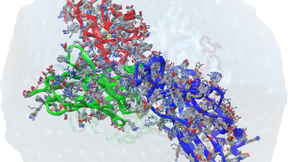
LLNL joins Human Vaccines Project to accelerate vaccine development and understanding of immune response
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has joined the international Human Vaccines Project (HVP), bringing Lab expertise and computing resources to the consortium to aid development of a universal coronavirus vaccine and improve understanding of immune response. The HVP is a nonprofit, public-private partnership with a mission to decode the human immune system and…
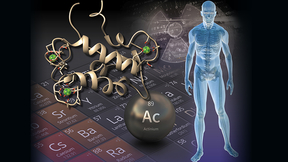
Cancer therapies and nuclear material detection get a boost from newly discovered protein
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Penn State scientists have demonstrated how a protein can be recovered and purified for radioactive metals like actinium that could be beneficial for both next-generation drugs used in cancer therapies and the detection of nuclear activities. Radioactive metals hold unique and essential places in a variety of medical…
Early access systems at LLNL mark progress toward El Capitan
Though the arrival of the exascale supercomputer El Capitan at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is still almost two years away, teams of code developers are busy working on predecessor systems to ensure critical applications are ready for Day One. Delivered in February, the “RZNevada” early-access system is providing experts at the National Nuclear Security…
Updated exascale system for earth simulations
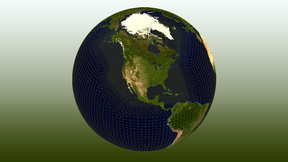
A new version of the Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM) is two times faster than its earlier version released in 2018. Earth system models have weather-scale resolution and use advanced computers to simulate aspects of Earth’s variability and anticipate decadal changes that will critically impact the U.S. energy sector in coming years. Version 2 of the Energy…
Four graduate students selected as Graduate Student Research Program recipients
Four graduate awardees selected by the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) program’s 2021 Solicitation 1 cycle will be hosted by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). The four graduate students are among 65 individuals representing 29 states who will conduct research at various DOE national laboratories. The students…
Making it count: Rebuilding infrastructure at the Nuclear Counting Facility
When Daniel Martin put the finishing touches on an autonomous vehicle robot, complete with an ultrasonic sensor to detect and evade obstacles, he knew he wanted to become an engineer. A high school student at the time, he was fascinated by the design and functionality of robots. Fast forward several years, and Martin is now a second-year electrical engineering Ph.D…
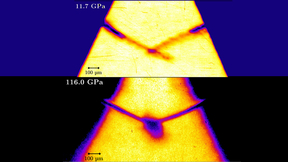
LLNL researchers observe laser-driven tin ejecta microjet interactions
The experimental observations of high-velocity particle-laden flow interactions has been sparse, given the difficulty of generating high-velocity flows of many particles. These observations play an important role in understanding a wide range of natural phenomena, ranging from planetary formation to cloud interactions. That is, until now. In experiments conducted at the…
Just how big was the 2020 Beirut explosion?
On Aug. 4, 2020, one of the largest non-nuclear explosions in history pulverized a Beirut port and damaged more than half the city. The explosion resulted from the detonation of tons of ammonium nitrate, a combustible chemical compound commonly used in agriculture as a high-nitrate fertilizer, but which can also be used to manufacture explosives. Since that time, the…
Climate change in the Sierra Nevada has profoundly altered its lake ecosystems
Climate change has significantly impacted the natural systems of the Sierra Nevada, including the mountain lakes that are an iconic part of California’s natural beauty. New research from a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist and colleagues from the University of Kentucky (UK) and Indiana State University (ISU) shows that lake-sediment cores from a…
Lab garners five technology commercialization grants
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and engineers have posted another banner year securing major grants through the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Technology Commercialization Fund (TCF). “I think the Laboratory did very well again, reflecting a variety of types and approaches to our research and development projects,” said Rich Rankin, the director of…
LLNL team wins $15 million to study how microbes affect carbon storage
Do dead microbes control the future of Earth’s climate? A team of researchers led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) suspects they might. Using new tools, the team can see which soil organisms are thriving and which are dying in California’s changing climate — and what happens to carbon in their cell biomass when they do. The seven-institution team has just…