Back
Space Science Institute
Where on Earth did the water come from?
Earth’s supply of water is incredibly important for its ability to sustain life, but where did that water come from? Was it present when Earth formed or was it delivered later by meteorites or comets from outer space? The source of Earth’s water has been a longstanding debate and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists think they have the answer — and they…
Pandora mission to study stars and exoplanets continues toward flight
The Pandora mission, co-led by a national laboratory and a NASA flight center, has passed a crucial step on its path to study stars and planets outside our solar system, or exoplanets. After a successful concept study report and system requirements review, NASA approved the mission to continue toward flight. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and NASA’s Goddard…
Lawrence Livermore takes part in NASA’s first planetary defense test
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is taking part in NASA’s first-ever planetary defense test, which deliberately collides a spacecraft into an asteroid called Dimorphos. The Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) will examine technologies that will prevent an impact of Earth by a hazardous asteroid. DART is the first demonstration of the kinetic impactor…
Data Science Challenge welcomes UC Riverside
Together with LLNL’s Center for Applied Scientific Computing, the Data Science Institute welcomed a new academic partner to the 2021 Data Science Challenge internship program: the University of California (UC) Riverside campus. The intensive program has run for three years with UC Merced, and it tasks undergraduate and graduate students with addressing a real-world…
A bigger nursery for the solar system’s first formed solids
The earliest solids formed in the solar system give clues to what radioactive species were made by the young sun, and which ones were inherited. By studying isotopic variations of the elements vanadium (V) and strontium (Sr), an international team of researchers including scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) found that those variations are not…
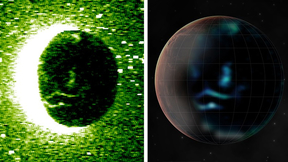
Lawrence Livermore optics used to spot elusive aurora on Red Planet
The United Arab Emirates' (UAE) Mars mission that launched about a year ago has recently captured the most detailed images of auroras in the Martian sky. The optics used to capture these images include a silicon carbide-coated mirror and diffraction grating for the Emirates Mars Ultraviolet Spectrometer (EMUS) that were developed by researchers at Lawrence Livermore…
Eyes High in the Skies
In 2021, a small satellite bearing an imaging payload featuring two MonoTeles hitched a rideshare on a SpaceX Starlink launch at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Planetary Research: Exploring Our Past and Future
How could life begin from a swirling chaos? How did Earth and its moon form? What can lunar rocks from the Apollo missions reveal? And what will scientists learn from exploration on distant moons? These questions are addressed in this four-part feature article on Lawrence Livermore’s space science research.
LLNL’s Tactically Responsive Launch-2 payload launched into orbit
When the U.S. Space Force’s Tactically Responsive Launch-2 (TacRL-2) mission launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base on June 13, it carried a payload designed and built in record time by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). LLNL provided a three-mirror reflective telescope and sensor for the payload, which they designed, integrated, tested and delivered within…
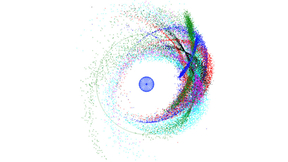
Virtual LLNL-UC Merced Data Science Challenge tackles asteroid detection though machine learning
Over three weeks, students from the University of California, Merced collaborated online with mentors at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) to tackle a real-world challenge problem: using machine learning to identify potentially hazardous asteroids that could pose an existential threat to humanity. The Data Science Challenge was the third such annual event for…
LLNL/Tyvak space telescope goes into orbit
Thousands of images of Earth and space have been taken by a compact space imaging payload developed by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers and its collaborator Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems. Known as GEOStare2, the payload has two space telescopes that together have taken more than 4,500 pictures for space domain awareness, astronomy and Earth…
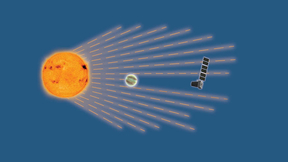
Lab will co-lead NASA mission to study stars, planets
NASA has selected Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) to serve as lead institutions for the Pandora scientific mission that will study 20 stars and their 39 exoplanets. The goal of the Pandora mission is to learn about starspots (akin to sunspots) and identify which of these exoplanets are hydrogen- or water-dominated and…
Lab has ties to Nobel Prize winner Andrea Ghez
The 2020 Nobel Prize in physics has been awarded to Andrea Ghez of the University of California, Los Angeles, and Reinhard Genzel of the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, for their discovery of the black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. They share the award with Roger Penrose of Oxford University for his mathematical proof that black holes are…
Inspiring future physicist while exploring dark energy
Doctoral student Victor Baules is spending his summer exploring the connection between dark energy and the expansion of our universe, but due to the pandemic, his research fellowship is more down-to-earth, taking place from his home in Alabama. Baules’ research trajectory in high-energy theory aligns with astrophysics research at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory …
Lawrence Livermore, Tyvak Systems announce agreement to develop telescopes for nanosatellites
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems Inc. have reached a cooperative research and development agreement (CRADA) to develop innovative compact and robust telescopes for nanosatellites. The four-year, $2 million CRADA will combine LLNL’s Monolithic Telescope (MonoTele) technology with Tyvak’s expertise producing high-reliability…
Lab physicist named astronomical society fellow
The American Astronomical Society (AAS) has selected Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist Peter Beiersdorfer as a fellow in its inaugural class of this accolade. The AAS fellows program was established in 2019 to confer recognition to AAS members for achievement and extraordinary service to the field of astronomy and the American Astronomical Society…
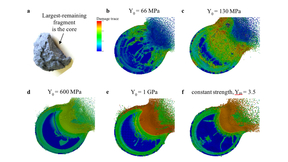
Planetary defenders validate asteroid deflection code
Planetary defense researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) continue to validate their ability to accurately simulate how they might deflect an Earth-bound asteroid in a study that will be published in the April issue of the American Geophysical Union journal Earth and Space Science. The study, led by LLNL physicist Tané Remington, also identified…
Lab physicist awarded 2020 dissertation prize
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) physicist Natalie Hell has been awarded the 2020 Dissertation Prize from the Laboratory Astrophysics Division (LAD) of the American Astronomical Society (AAS). Hell received the prize for her outstanding experimental doctoral dissertation in laboratory astrophysics. Her thesis, “Benchmarking Transition Energies and Emission…
Gemini Plus Enables Next-Generation Planetary Composition Measurements
NASA has funded the development of a new high-purity germanium gamma-ray detector—the GeMini Plus—for use in upcoming planetary exploration missions.
Big Data Illuminates the Physical Sciences
Astrophysics is a growth area in the Laboratory’s advancement of basic science for national and global security needs. In this field, data science helps researchers catalog and interpret objects orbiting Earth and process huge volumes of data captured by ground- and space-based telescopes.