Back
Computing
Researchers measure electron emission to improve understanding of laser-based metal 3D printing
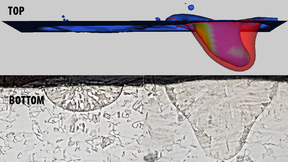
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have taken a promising step in improving the reliability of laser-based metal 3D printing techniques by measuring the emission of electrons from the surface of stainless steel during laser processing. Researchers collected thermionic emission signals from 316L stainless steel under laser powder bed fusion (LPBF)…
Lab scientists among most cited researchers worldwide
Fifty-seven researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) were among the top 2 percent of the most cited researchers worldwide throughout their careers, according to research on metascience by Stanford University. Metascience is the "study of studies" using scientific methods. Stanford University professor John Loannidis worked alongside U.S.-based Kevin…
Examining climate effects of regional nuclear exchange
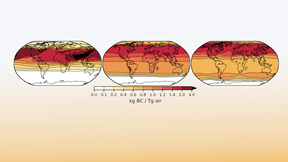
A team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers has found that the global climatic consequences of a regional nuclear weapons exchange could range from a minimal impact to more significant cooling lasting years. The five LLNL scientists examined the potential for global climate changes from large urban fires ignited in a hypothetical regional nuclear…
Girls Who Code – ‘Big’ program goes virtual
Livermore High School freshman Amber Belk is focused on studying chemical engineering in college, but through the Girls Who Code – "Big" program, she gained a new appreciation for how high performance computers that can model the types of molecules she will be studying. “Writing software codes and using the Linux operating system was really fun,” Belk said. "I really…
LLNL, IBM win SC20 ‘Test of Time’ for Blue Gene/L
A team of current and former Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and IBM scientists won the annual “Test of Time” award at the 2020 Supercomputing Conference on Nov. 19 for a paper outlining LLNL’s Blue Gene/L supercomputer. Published by the Supercomputing Conference in 2002, the paper was the first peer-reviewed overview article to disclose details of Blue Gene…
The Sierra Era
Lawrence Livermore’s high-performance computing (HPC) facilities house some of the fastest supercomputers in the world, including the flagship Sierra machine. Online for more than a year, Sierra primarily runs simulations for the National Nuclear Security Administration’s (NNSA’s) Advanced Simulation and Computing (ASC) Program. Sierra substantially increases the…
HPC4Energy Innovation kicks off fall 2020 solicitation
The High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) Program, managed by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), is seeking new industry proposals for short-term projects that could benefit from world-class DOE high performance computing (HPC) and expertise. Under the fall 2020 HPC4EI solicitation, DOE’s Office of…
3D-printed glass enhances optical design flexibility
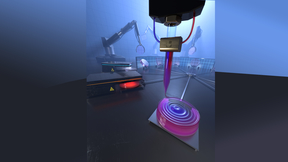
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have used multi-material 3D printing to create tailored gradient refractive index glass optics that could make for better military specialized eyewear and virtual reality goggles. The new technique could achieve a variety of conventional and unconventional optical functions in a flat glass component (with no surface…
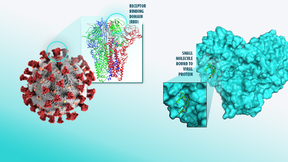
Model for COVID-19 drug discovery a Gordon Bell finalist
A machine learning model developed by a team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists to aid in COVID-19 drug discovery efforts is a finalist for the Gordon Bell Special Prize for High Performance Computing-Based COVID-19 Research. Using Sierra, the world’s third fastest supercomputer, LLNL scientists created a more accurate and efficient generative…
Lab stands tall on bi-annual list of Top500 supercomputers
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) can lay claim to housing four of the world’s 100 most powerful supercomputers, more than any other institution according to the TOP500 List announced Monday during the virtual Supercomputing 2020 conference (SC20). The 125-petaFLOP peak Sierra, the National Nuclear Security Administration’s flagship supercomputer, remained…
Lab stands tall on bi-annual list of Top500 supercomputers
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) can lay claim to housing four of the world’s 100 most powerful supercomputers, more than any other institution according to the TOP500 List announced Monday during the virtual Supercomputing 2020 conference (SC20). The 125-petaFLOP peak Sierra, the National Nuclear Security Administration’s flagship supercomputer, remained…
Corona supercomputer gets funding for COVID-19 work
With funding from the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), chipmaker AMD and information technology company Supermicro have upgraded the supercomputing cluster Corona, providing additional resources to scientists for COVID-19 drug discovery and vaccine research. The recent addition of nearly 1,000 AMD…
DOE announces five new energy projects at LLNL
The Department of Energy (DOE) today announced two rounds of awards for the High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation Program (HPC4EI), including five projects at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). HPC4EI connects industry with the computational resources and expertise of the DOE national laboratories to solve challenges in manufacturing, accelerate…
LLNL welcomes 'Ruby' supercomputer for national nuclear security mission and COVID-19 research
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), along with partners Intel, Supermicro and Cornelis Networks, have deployed “Ruby,” a high performance computing (HPC) cluster that will perform functions for the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) and support the Laboratory’s COVID-19 research. Funded by NNSA’s Advanced Simulation and Computing (ASC) program, the…
LLNL, partners open access to CO2 storage simulator
After more than two years of joint research, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Total and Stanford University are releasing an open-source, high-performance simulator for large-scale geological carbon dioxide (CO2) storage. The GEOSX simulator will enable researchers around the world to build on the work of the three partners, providing an open framework to…
Department of Energy to showcase scientific computational expertise at SC20
The scientific computing and networking leadership of 17 Department of Energy (DOE) national laboratories will be showcased at SC20, the International Conference for High-Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, taking place Nov. 9-19 for the first time via a completely virtual format. Like most conferences and workshops being held this year across the U.S…
Women’s math association names Woodward fellow
The Association for Women in Mathematics (AWM) announced it has named Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) computational scientist Carol Woodward as a 2021 fellow, recognizing her commitment to supporting and advancing women in the mathematical sciences. A computational mathematician in the Center for Applied Scientific Computing (CASC) since 1996, Woodward’s…
Lab explores new resins for light-based 3D printing
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has simulated the cross-linking of 3D-printed polymer networks, a key step toward developing new functional resins for light-based 3D-printing techniques including two-photon lithography (TPL) and volumetric additive manufacturing (VAM). The team used molecular dynamics simulations to study, at a microscopic level, the…
Mammoth computing cluster to aid COVID research
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and its partners AMD, Supermicro and Cornelis Networks have installed a new high performance computing (HPC) cluster with memory and data storage capabilities optimized for data-intensive COVID-19 research and pandemic response. Funded by the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act, the “big memory” cluster,…
AI gets a boost via LLNL, SambaNova collaboration
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has installed a state-of-the-art artificial intelligence (AI) accelerator from SambaNova Systems, the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) announced today, allowing researchers to more effectively combine AI and machine learning (ML) with complex scientific workloads. LLNL has begun integrating the new AI hardware,…